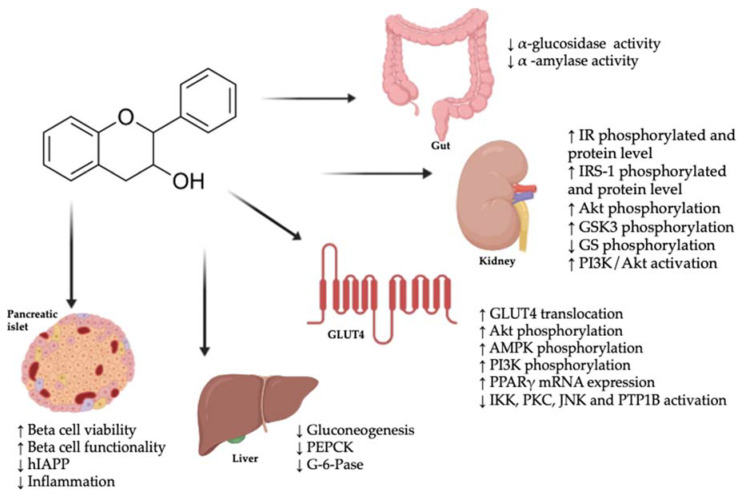
Figure 1.
Potential molecular mechanisms underlying the antidiabetic properties of flavan-3-ols. ↑: increase; ↓: decrease; Akt: protein kinase B; AMPK: 5’ adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; G-6-Pase: glucose-6-phosphatase; GLUT4: glucose transporter type 4; GS: glycogen synthase; GSK3: glycogen synthase kinase 3; hIAPP: human islet amyloid polypeptide; IKK: IκB kinase; IR: insulin receptor; IRS-1: insulin receptor substrate 1; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinases; mRNA: messenger RNA; PEPCK: phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PKC: protein kinase C; PPARγ: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ; PTP1B: protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B.