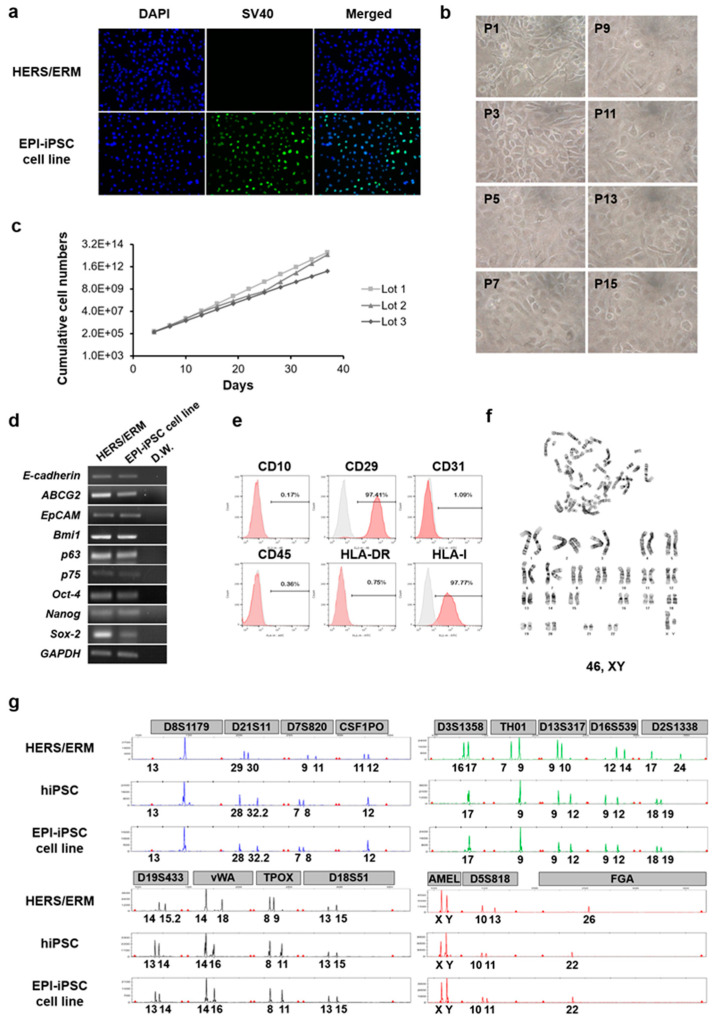
Figure 4.
Characterization of dental epithelial-like stem cell lines derived from hiPSC. (a) Immunofluorescence staining for the expression of SV40 in the EPI-iPSC cell line. Primary HERS/ERM cells did not express SV40, whereas the established EPI-iPSC cell line expressed SV40. (b) Morphology and passaging of the EPI-iPSC cell line. EPI-iPSC-SV40 showed the typical epithelial cell-like shape and clonal expansion until passage 15. The morphology was maintained through subculture. Magnifications are at 400×. (c) Growth of three EPI-iPSC-SV40 lines. Cumulative cell numbers of EPI-iPSC showed that they maintained stable proliferation for 40 days. (d) Expression of epithelial stem cell and stemness-related genes in the EPI-iPSC cell line (passage 10). EPI-iPSC cell line was positive for E-cadherin, ABCG2, EpCAM, Bmi1, p63, and P75, which are epithelial stem cell markers, and Oct-4, Nanog, and Sox-2, which are stemness-related markers. (e) FACS analysis of the EPI-iPSC cell line (passage 10). EPI-iPSC was positive for CD29 and HLA-I, and negative for CD10, CD45, HLA-DR, and CD31. (f) Karyotype of the EPI-iPSC cell line. The EPI-iPSC cell line at passage 10 showed a normal karyotype with 46, XY. (g) Origin of the EPI-iPSC cell line. Microsatellite (STR) analysis, which is a PCR-based microsatellite method, showed that the differentiated EPI-iPSC cell line was derived from hiPSC. All data were obtained from three replicates.