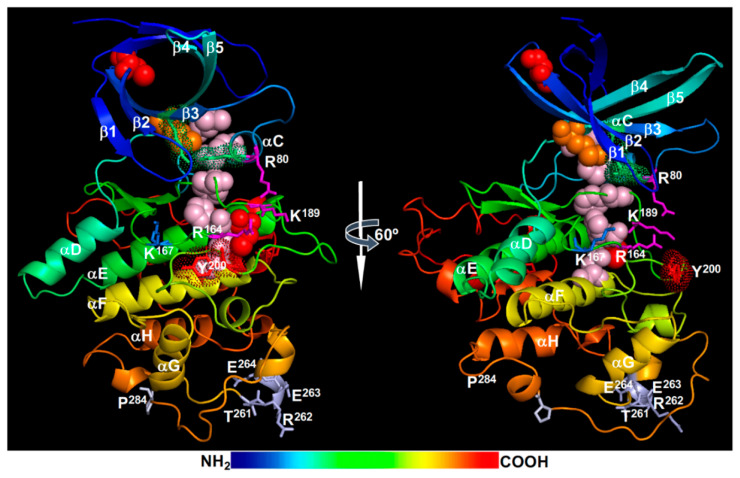
Figure 5.
A structural model of BIN2. Shown here are two rotational (0° and 60°) views of a modeled BIN2 structure obtained at SWISS-MODEL (https://swissmodel.expasy.org/). Individual β-strands (β1-β5) and α-helices (αC-αH) were labeled. The two extra antiparallel-β-strands that cap the N-lobe are not labelled. The TREE motif and the Pro284 residue mutated in known bin2/dwarf12/ucu1 alleles are indicated with grey-colored sticks. The magenta sticks show the three positively charged residues [Arg80, Arg164, and Lys189 (also acetylated)] of the conserved phosphate-binding pocket, the red sticks with red dots denote the Tyr200 residue, the green sticks with green dots mark the Lys69-Glu81 salt bridge between the β3-strand and the αC-helix, and the blue sticks represent the Lys167 residue that corresponds to the acetylated Lys183 residue of the human GSK3β. The red spheres show the Cys residues that were shown to be S-nitrosylated or S-glutathionylated in vitro, the orange spheres indicate the gatekeeper Met115 residue, and the pink spheres mark the 5 R-spine residues (from lower to top: Asp223, His163, Phe185, Met85, and Leu96). Important residues are also labelled with single letter codes with positions. The rainbow bar indicates the order of AAs from the N-terminus (blue) to the C-terminus (red).