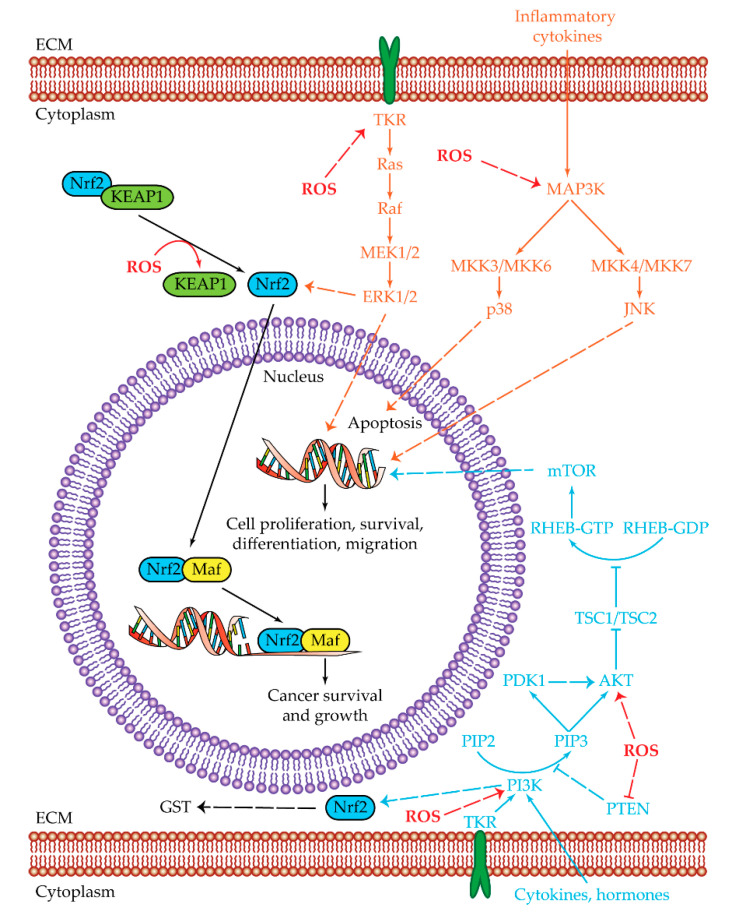
Figure 2.
Oxidative stress pathways. Summarized are the two main pathways of cell proliferation and survival subjected to reactive oxygen species (ROS) regulation: MAPK (orange) and PI3K/AKT/mTOR (light blue). The shared Nrf2 pathway is highlighted in black, while ROS regulations/interactions are visualized in red. Positive regulations are pictured as dotted arrows, and negative regulations are pictured as dotted truncated arrows. High oxidative stress is one of the key aspects that in normal conditions leads to cell death. HCC cells can manage ROS overproduction by activating the MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways. The last effectors of MAPK pathways are ERK1/2, JNK, and p38. ERK1/2 and JNK are upregulated and lead to the transcription of genes involved in cell proliferation, survival, differentiation, and migration, while p38 is related to apoptosis and in HCC cells is downregulated. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is upregulated in HCC cells leading to cell proliferation, survival, differentiation, and migration. ROS can regulate PI3K and AKT activities by increasing their phosphorylation or by decreasing PTEN levels. Both MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways have a common effector which is Nrf2. Nrf2 is a transcription regulator which is maintained at low levels by the KEAP1 protein. In the presence of high ROS levels, KEAP1 dissociates from Nrf2, which by this dissociation becomes capable of reaching the nucleus. Once inside the nucleus, Nrf2 heterodimerizes with Maf. The Nrf2/Maf heterodimer binds the antioxidant-responsive elements for the transcription of genes involved in cancer cell survival and growth. Nrf2 is also able to activate genes related to oxidant homeostasis such as glutathione S-transferase (GST). Abbreviations: AKT = protein kinase-B; ECM = extracellular matrix; ERK1/2 = extracellular regulated kinases 1 and 2; JNK = c-Jun N-terminal kinases; KEAP1 = Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; GST = glutathione S-transferase; Maf = musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma protein; MAP3K = MAPK kinase kinase ; MEK1/2 = MAP/ERK kinases 1 and 2; MKK3/6 and MKK 4/7 = mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3/6 and 4/7; mTOR = mammalian target of rapamycin; Nrf2 = nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; p38 = p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases; PDK1 = serine/threonine kinase phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1; PI3K = phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PIP2 = phosphatidylinositol 4,6-bisphosphate; PIP3 = phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate; PTEN = phosphatase and tensin homologue; Raf = rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma protein; Ras = rat sarcoma protein; RHEB = Ras homolog enriched in brain; ROS = reactive oxygen species; TKR = tyrosine-kinase receptor; TSC1/TSC2 = tuberous sclerosis proteins 1 and 2 complex. 3.2. Nrf2 and Oxidative Stress.