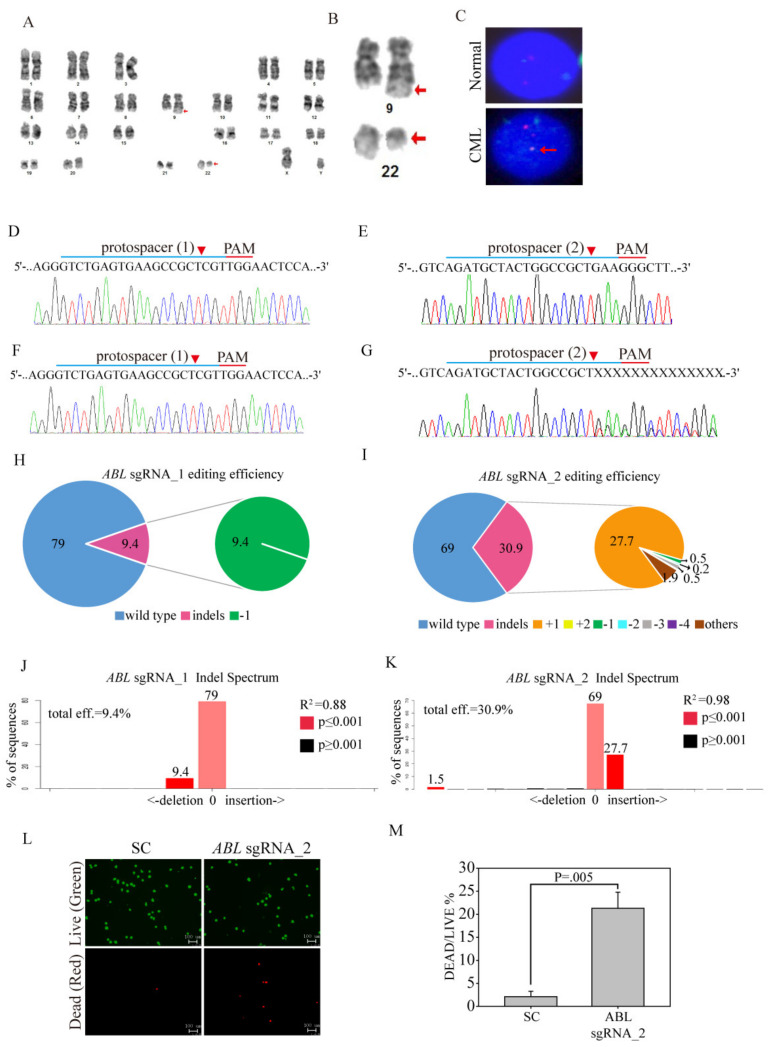
Figure 5.
Ex vivo ABL-targeted CRISPR/Cas9 lentivirus therapy of CML patients. (A) Karyogram from the products of conception showing the karyotype of 46, XY, t(9;22)(q34;q11.2). (B) Highlight of chromosomes 9 and 22 at the same level of resolution. (C) Interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis using probes for the BCR (green) and ABL genes (red) shows an abnormal pattern t(9;22) of the fusion protein (yellow, lower panel) in the CML patient cells compared to the normal cells (separate colors). SC sgRNA and ABL sgRNAs were delivered to the clinical CML cells by lentivirus. After transduction, DNA from the virus-infected cells was purified and subjected to Sanger sequencing for the target sites of (D) ABL sgRNA_1 and (E) ABL sgRNA_2 in the SC sgRNA-transfected CML cells. (F) ABL sgRNA_1 and (G) ABL sgRNA_2 produced a mixture of sequences around the expected Cas9 cleavage site in a pool of gene-edited cells after ABL sgRNA lentivirus transduction. TIDE algorithm analysis of the ABL gene-edited sequence showed a high editing efficiency in clinical CML cells. The pie charts show the percentages of indels in the ABL gene edited by (H) ABL sgRNA_1 and (I) ABL sgRNA_2. The gene editing efficiency of the two sgRNAs is presented in red, while the two most common -1 and +1 indels are presented in green and orange, respectively. The original TIDE algorithm analysis is shown for (J) ABL sgRNA_1- and (K) ABL sgRNA_2 virus-transfected CML cells compared to SC-transfected cells. (L) The LIVE/DEAD cell viability assay was performed after SC sgRNA and ABL sgRNA_2 were delivered to the clinical CML cells by lentivirus. Cells were subjected to viability assays to identify live (green) and dead (red) cells. (M) Cell death after SC sgRNA and ABL sgRNA_2 lentivirus delivery was analyzed for significance. Data were analyzed with Student’s t-test; all p-values were two-sided.