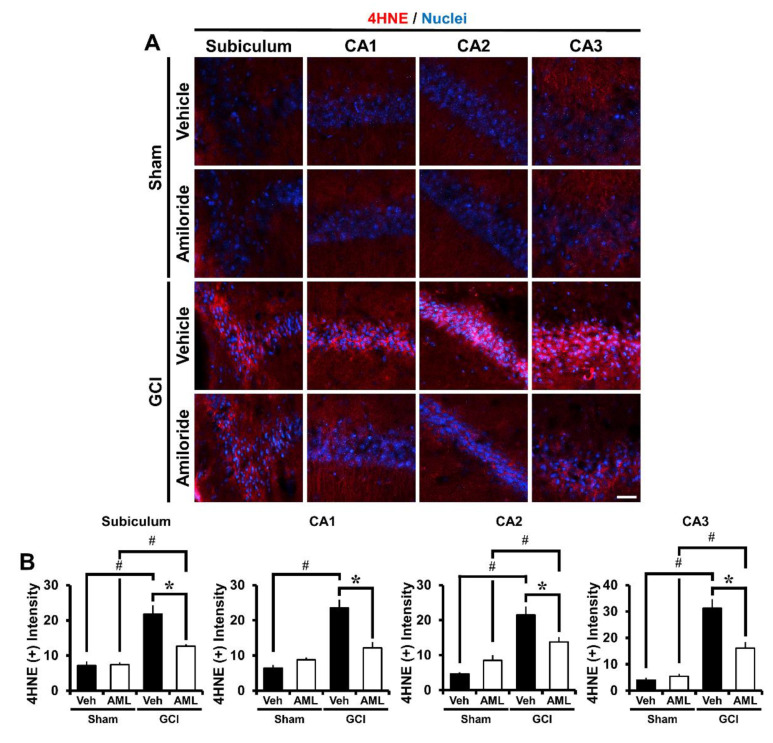
Figure 3.
Amiloride reduced oxidative injury after GCI. Oxidative injury was detected by 4-hydroxynonenal (4HNE, red color) staining from the hippocampal Sub, CA1, CA2, and CA3 regions 24 h after GCI. (A) Sham-operated groups showed minimal 4HNE fluorescence signals in the hippocampus. Amiloride-treated groups showed reduced immunoreactive fluorescence intensity for 4HNE in the hippocampus compared with the vehicle-treated group after GCI. Scale bar = 20 μm. (B) The bar graph presents the 4HNE fluorescence intensity in the Sub, CA1, CA2, and CA3 regions. The fluorescence intensity showed a significant difference among groups (sham-vehicle, n = 6; sham-amiloride, n = 5; GCI-vehicle, n = 8; GCI-amiloride, n = 8). Data are mean ± S.E.M. * Considerably different from the vehicle-treated group, p < 0.05; # sham versus vehicle-operated group, sham versus vehicle-treated group, p < 0.05. (Kruskal–Wallis test (B) Sub: Chi square = 22.444, df = 3, p < 0.001; CA1: Chi square = 17.896, df = 3, p < 0.001; CA2: Chi square = 20.967, df = 3, p < 0.001; CA3: Chi square = 20.986, df = 3, p < 0.001).