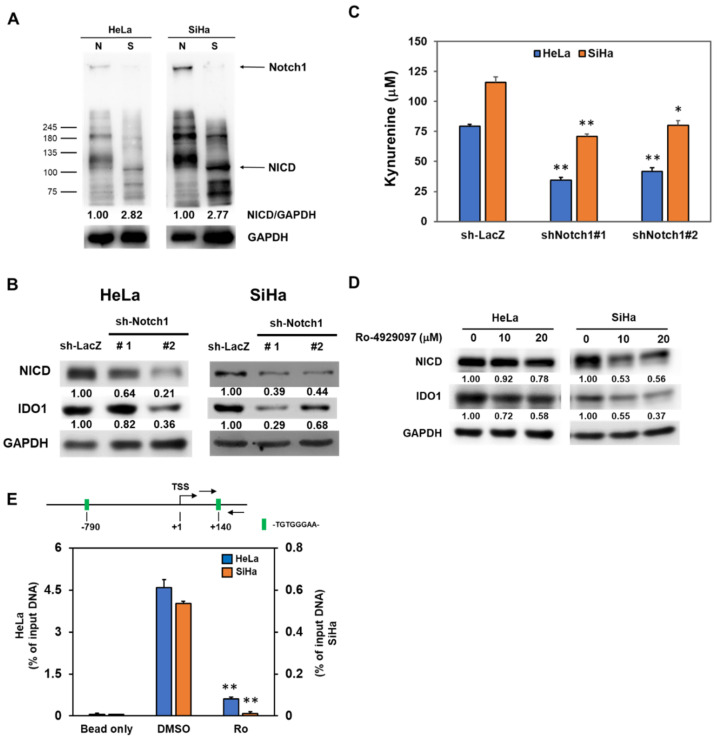
Figure 3.
Notch1 activation in cervical CSCs participates to the IDO1 induction. (A) Total cell lysates were collected from conventional adherent culture (N) or tumorspheres (S) from HeLa and SiHa cells and the expression of Notch1 and NICD was determined by Western blotting. (B–D) Tumorspheres from HeLa and SiHa cells were dissociated into single cell suspension and were transduced with lentiviruses carrying Notch1 specific shRNAs (sh-Notch1#1 or sh-Notch1#2) followed by puromycin selection. The surviving cells were collected and detected the expression of NICD or IDO1 by Western blotting (B). The insert numbers indicate the relative expression level in comparison to sh-LacZ transduced cells. The kynurenine concentration in the culture supernatant was determined by Ehrlich’s reagent (C). * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01. Tumorsphere cells were treated with Ro-4929097 as the indicated concentration and detected the expression of NICD or IDO1 by western blot (D). The insert numbers indicate the relative expression level in comparison to 0.1% DMSO control (labeled as 0 μM). (E) The putative binding site of RBPJ/CSL (-TGTGGGAA-) in IDO1 promoter was analyzed by the Eukaryotic Promoter Database (EPD) website and the binding of NICD to the RBPJ/CSL binding site of IDO1 promoter at +140 site in HeLa and SiHa tumorsphere cells was detected by the chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) method with an anti-Notch1 antibody and quantitated by the qPCR method. Data were presented as percentage of input DNA. ** p < 0.01. All the experiments were repeated three times and the data from one experiment were presented.