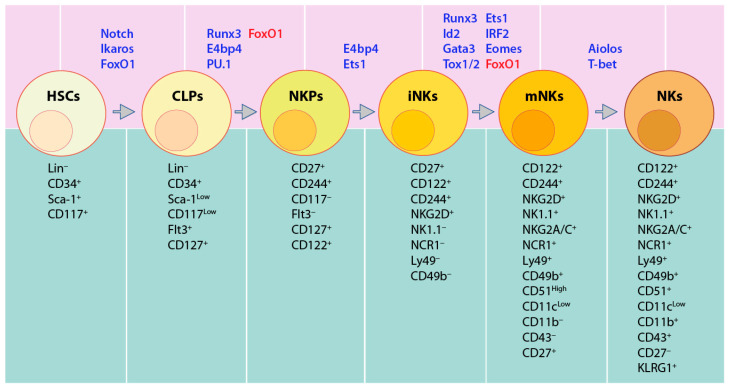
Figure 2.
Transcription Factors (TFs) involved in distinct murine NK cell developmental stages. Notch and Ikaros promote Lineage negative (Lin−) CD34+Sca-1+CD117+ hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) committing to common lymphoid progenitors (CLPs, Lin−CD34+Sca-1LowCD117LowFlt3+), while FoxO1 suppresses this commitment to keep the HSCs in a quiescent state. Runx3, E4bp4, PU.1, and Id2 enhance NK cell lineage transition to CD27+CD244+CD127+CD122+ NK cell precursors (NKPs). FoxO1 suppresses NK lineage transition. Committed immature NK cells (iNKs) that are marked by the expression of NKG2D are regulated by E4bp4 and Ets1. Runx3, Ets1, Id2, IRF2, Gata3, Eomes, and Tox1/2 promote the iNK into mature NK cells (mNKs), which are defined by the expression of NCR1, NK1.1, Ly49, CD49b, and CD51. Aiolos and T-bet further enhance mNK to terminal NK cells (tNK) with the expression of CD11b, Ly49s, and KLRG1 and loss of CD27.