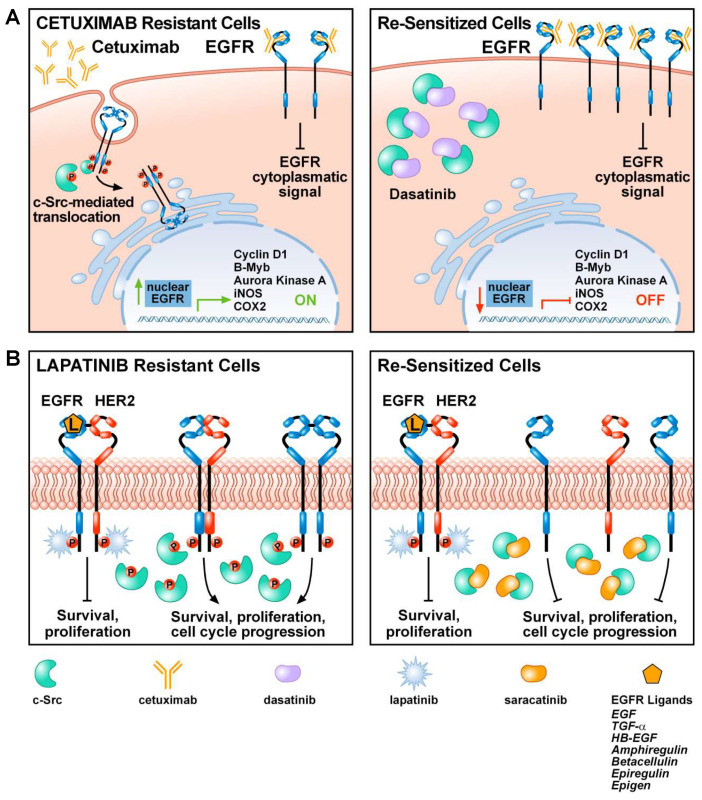
Figure 1.
c-Src mediates mechanisms of resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors: (A) Cetuximab resistant cells express high levels of c-Src protein. Although cetuximab might abrogate EGFR signaling from the plasma membrane, most EGFRs are translocated to the nucleus in a Src-dependent manner. Here, EGFR activates proliferative signals by modulating Cyclin D1, B-myb, Aurora kinase K, INOS, COX2 (left panel). c-Src inhibition with dasatinib reduces EGFR nuclear translocation, re-sensitizing cells to cetuximab treatment (right panel). (B) In lapatinib resistant breast cancer cells, c-Src over-expression induces EGFR/HER2 heterodimers activation, bypassing the lapatinib-dependent inhibition of survival and proliferation pathways. In particular, c-Src phosphorylation of EGFR Y845 boosts down-stream signaling pathways to EGFR homo and heterodimers activation (left panel). Cell treatment with c-Src inhibitor saracatinib restores lapatinib sensitivity and overcome EGFR and its related oncogenic pathways activation (right panel).