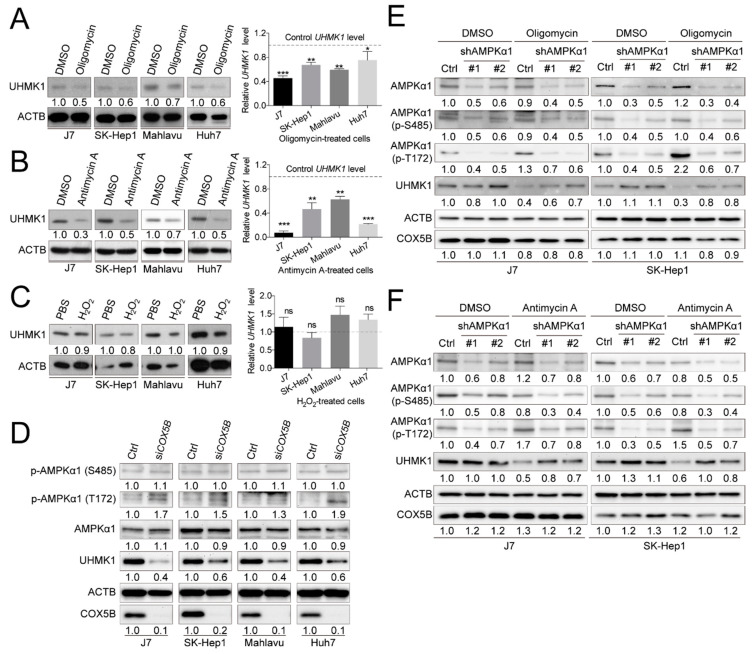
Figure 6.
COX5B-mediated bioenergetic alteration modulating UHMK1 expression is AMPK activation-dependent. Western blot and RT-qPCR analysis of cell lysates derived from cells treated with (A) oligomycin, (B) antimycin A and (C) H2O2. Oligomycin and antimycin A were used for blocking bioenergy production. H2O2 was used for accumulating ROS. The western blot images in this panel were acquired by exposing the luminescent signals to X-ray films, except for those of the Antimycin-treated Mahlavu cell, which was obtained by using chemStudio PLUS imaging system. The p value was derived from paired two-tail student t-test. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ns, not significant. (D) The relationship between depletion of COX5B and activation of AMPK was assessed by western blot. AMPK T172 phosphorylation indicated activation while S485 phosphorylation was considered suppression of enzyme activities. The combined analysis of the relationship between bioenergetic alteration, induction by (E) oligomycin and (F) antimycin A, and activation of AMPK in modulation of UHMK1 expression. The western blot images in (D–F) were all acquired by using chemStudio PULS imaging system. All the in vitro cell-based assays shown in this figure were conducted in duplicates.