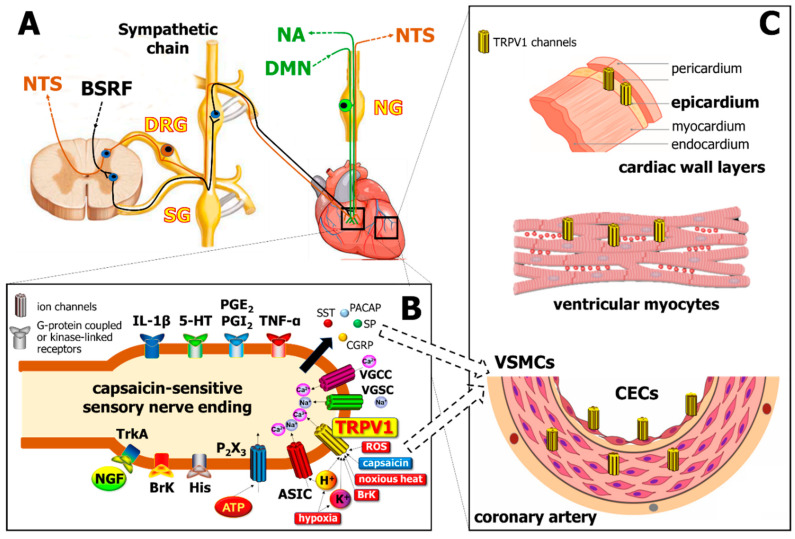
Figure 1.
Localization of the transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) channel in different cells of the cardiovascular system. Panel (A): Cell bodies of primary sensory neurons innervating the heart are localized in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) and transmit sensory signals to the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS), as well as act as sensory efferents in the heart and the vasculature. Sensory nerves are coupled anatomically to sympathetic nerves which are derived from the brain stem reticular formation (BSRF), as well as to the vagus nerve (green), which projects afferents to the nucleus ambiguus (NA) and possesses motor efferents from dorsal motor nucleus (DMN). SG, sympathetic ganglion; NG, nodose ganglion. Panel (B): Several receptors co-localized with TRPV1 on the capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerve endings, which mediate a myriad of inflammatory signals including cytokines like tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and interleukins (e.g., IL-1β), bradykinin (BrK), histamine (His), nerve growth factor (NGF; acting on Tropomyosin receptor kinase A—TrkA receptors), prostaglandins (e.g., PGE2, PGI2), serotonin (5-HT), and purine mediators (acting at P2 × 3 purinergic receptors). Noxious stimuli such as ischemia/hypoxia, increased level of reactive oxygen species (ROS), noxious heat (> 43 °C), increased levels of K+ or H+ activate TRPV1, and H+ also stimulate acid-sensitive ion channels (ASIC). Further ion channels, such as voltage-gated Na+ and Ca2+ channels (VGSC, VGCC) may also increase intracellular Na+ and Ca2+ levels, thereby inducing the release of peptide mediators, including calcitonin gene related peptide (CGRP), substance P (SP), somatostatin (SST), and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP). Panel (C) demonstrates the localization of TRPV1 channels on different cell types of the heart (CECs, cardiac endothelial cells; VSMCs, vascular smooth muscle cells).