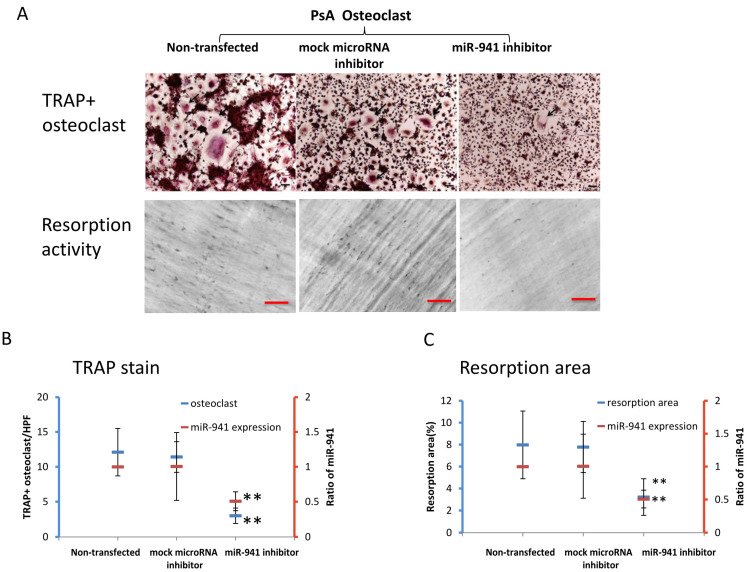
Figure 3.
miR-941 inhibitor reversed osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption activity in patients with PsA. The CD14+ monocytes were obtained from eight PsA patients and were subsequently activated into osteoclasts with treatment of M-CSF for 72 h. Cells were either nontransfected or transfected with the control-microRNA inhibitor or miR-941 inhibitor followed by TNF-α and RANKL very three days for nine days to study their ability to form osteoclasts and their activity of bone resorption. At day 13, the number of osteoclast formations and percentage of resorption pits were measured. (A) The cells were stained with TRAP to calculate the number of osteoclasts among non-transection, negative control miRNA and miR-941 inhibitor transfection groups, Scale bar: 50 μm. For the evaluation of resorption activity, the resorption pits were recorded by a bright field microscope, Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) The number of osteoclasts was quantified among the three groups (blue). The relative expression of miR-941, as standardized to the level of non-transfected osteoclasts, was depicted as orange color. (C) The eroded surface areas on the dentine slice were quantified using ImageJ software as percentage of expressions in total areas (blue line). The expressions of miR-941 in the osteoclasts were measured by qRT-PCR to evaluate the effect of miR-941 inhibitors transfection. The relative expression of miR-941, as standardized to the level of non-transfected osteoclasts, was depicted as orange color. ** p < 0.01.