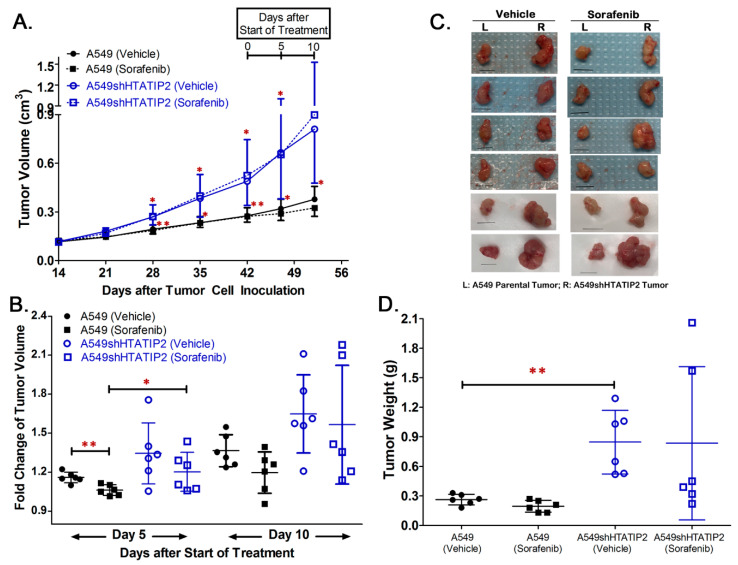
Figure 3.
A549shHTATIP2 tumors exhibited rapid growth and reduced sensitivity to sorafenib treatment in vivo. Male athymic nude mice bearing both subcutaneous A549 parental (on the left flank) and A549shHTATIP2 (on the right flank) tumors received oral administration of either vehicle or 40 mg/kg/day of sorafenib for 10 consecutive days (n = 6 per group). (A). Comparison of tumor growth between A549 parental and A549shHTATIP2 tumors. Once daily sorafenib treatment at 40 mg/kg was started on Day 43 after tumor inoculation. (B). Fold change of tumor volume was compared between A549 and A549shHTATIP2 tumors and between vehicle and sorafenib treatment groups on Day 5 and Day 10 after the start of the treatment. Fold change of tumor volume was calculated as the ratio of tumor volume measured on Day 5 and Day 10 of the treatment period to that measured on Day 0 prior to the start of the treatment. (C). Subcutaneous tumors harvested from the vehicle and sorafenib treatment groups. Scale bar, 1 cm. (D). Comparison of tumor weights between A549 and A549shHTATIP2 tumors in the presence and absence of sorafenib treatment. Results are presented as mean ± SD. SD is denoted by the error bars. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 compared between A549 parental and A549shHTATIP2 tumors receiving the same treatment or between vehicle and sorafenib treatment in the same type of tumor using the two-sample t-test.