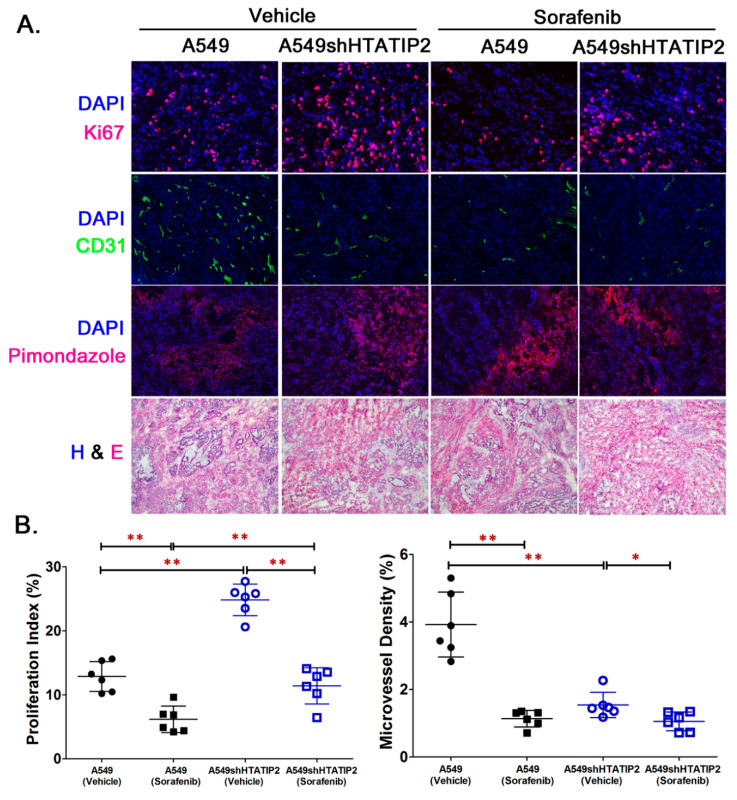
Figure 5.
The aggressive phenotype of A549shHTATIP2 tumors was associated with increased number of proliferating cells and stalled tumor angiogenesis insensitive to sorafenib treatment. (A). Representative images for immunofluorescence staining for Ki67, CD31 and pimonidazole in tumor sections from individual groups. The nuclei were stained with 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Original magnifications, × 200. Immunofluorescence staining for pimonidazole indicated the existence of hypoxia in all tumor xenografts. The H&E staining was performed to assess tumor section integrity that might be affected during cryosectioning and fixation in 4% PFA. (B). Quantification of Ki67 and CD31 immunofluorescence staining showed increased number of proliferating cells and reduced micro-vessel density (MVD) in the vehicle-treated A549shHTATIP2 tumors. Sorafenib treatment significantly decreased the number of proliferating cells in both A549 and A549shHTATIP tumors and the MVD in A549 tumors, but had no effect on the MVD in A549shHTATIP2 tumors. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Error bars are SD. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 compared between A549 parental and A549shHTATIP2 tumors receiving the same treatment or between vehicle and sorafenib treatment in the same type of tumor using the two-sample t-test.