Figure 3.
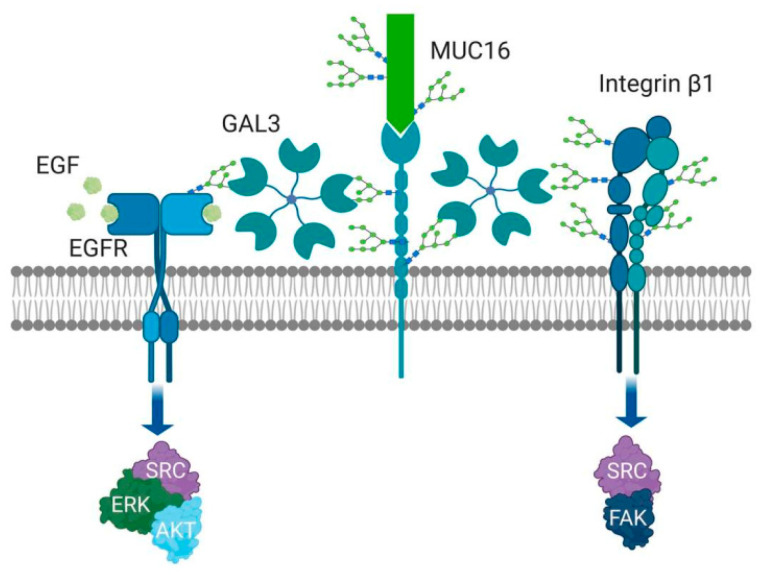
Gal-3 is involved in cell adhesion regulation, migration, invasion, angiogenesis, and metastasis. The specific extracellular Gal-3 function depends on the polymerization of Gal-3 into pentameric complexes. The action of Galectin 3 depends on glycan binding partners. These complexes link to glycans of high complexity (e.g., N-glycosylation lactosamine tetra-antennary forms and the Thomsen–Fredenreich antigen on O-glycans, especially in cancer. Through carbohydrate binding and polymerization to pentamers, Gal-3 forms a lattice and regulates the position of growth factor receptors, including EGFR, integrins and proteins like MUC16.