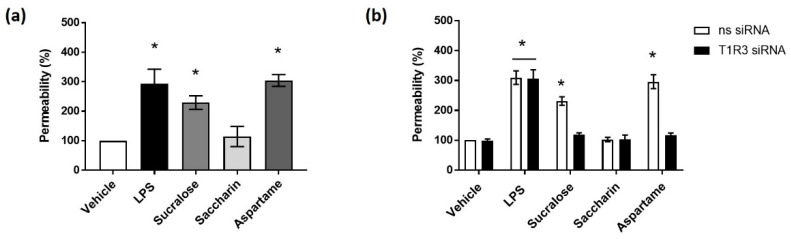
Figure 2.
Low physiological concentrations of artificial sweeteners sucralose and aspartame disrupt the intestinal epithelial barrier through the sweet taste receptor. (a) The permeability of the epithelial monolayer was measured with an FITC-dextran assay, following exposure to sucralose, saccharin, and aspartame (0.1 mM) for 24 h using lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (1 µg/mL) as a positive control. (b) The permeability of the Caco-2 cell monolayer was measured with an FITC-dextran assay following the siRNA knockdown of T1R3 for 24 h and exposure to sucralose, saccharin, and aspartame (0.1 mM) for a further 24 h. % permeability was calculated normalized to vehicle treatment. n = 6. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. * p < 0.05 versus vehicle (0 µM).