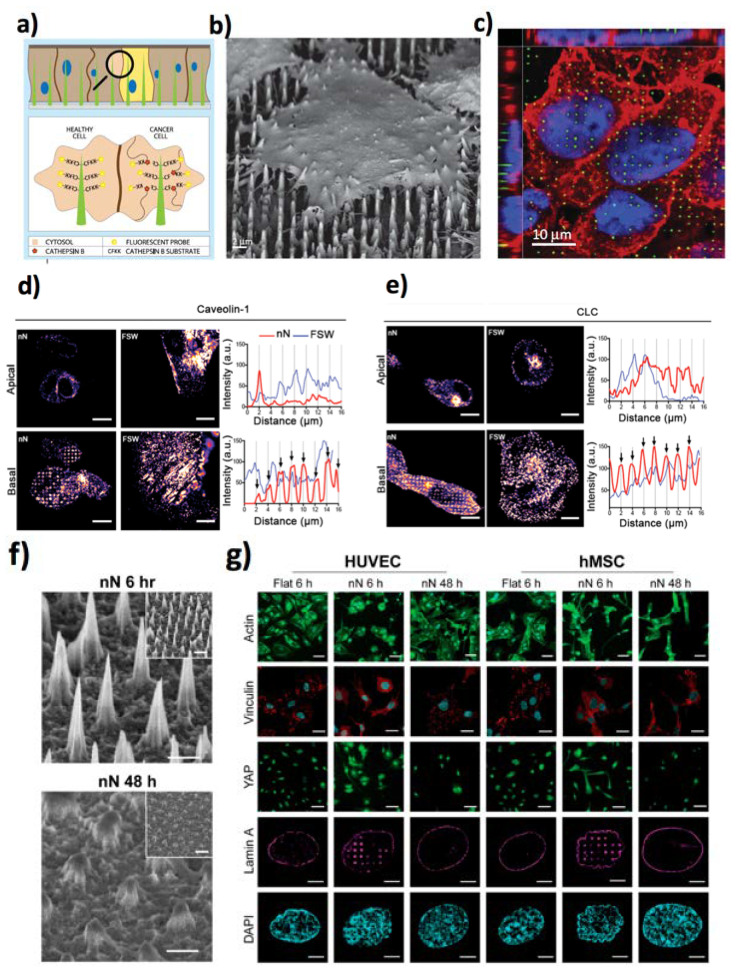
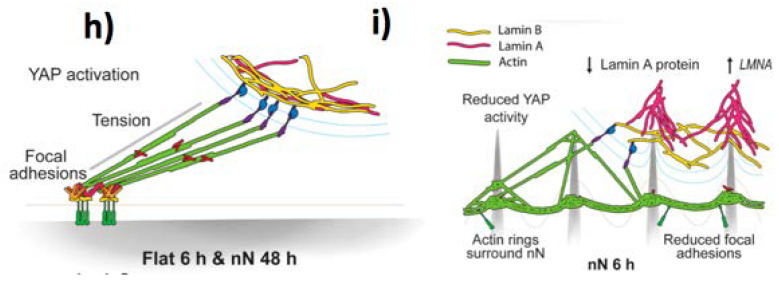
Figure 2.
Si NWs-based single-cell stimulation and mechanosensing. (a) An NW-based sensor for cathepsin, relying on the CTSB cleaving its CFKK peptide substrate, freeing the linked TAMRA fluorescent probe. (b) Scanning electron microscopy and (c) laser scanning confocal fluorescence microscopy image of a cell onto NWs. NWs in green, cell membrane in red, nucleus in blue. Reproduced from ref. [48] under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license (CC BY). (d) Fluorescence confocal microscopy images of cell scaffolding protein Caveolin-1 and (e) clathrin (CLC) protein accumulation after 6 h in the membrane of hMSCs cultured on Si NWs. Scale bars are equal to 10 µm. Reproduced from ref. [49] under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license (CC BY). (f) Si NNs degradation after 48 h in cell culture. Scale bars are 1 μm, and 2 μm in the inset. (g) Restoration of cell phenotype on degraded NNs as compared to flat control substrates at 6 h. Cellular actin cytoskeleton (green: phalloidin, scale bars are 50 μm), dense staining of vinculin-rich focal adhesions (red: vinculin, cyan: DAPI, scale bars are 25 μm), nuclear localization of YAP (green, scale bars are 50 μm), and an unmodified nucleus (magenta: lamin A, cyan: DAPI, scale bars are 5 μm). (h) Intracellular tension on flat surfaces due to focal adhesion formation, yielding YAP nuclear localization. (i) Decreased focal adhesion of cells onto NNs triggers the generation of actin ring, and nuclear confinement of lamin A and B. Adapted with permission from ref. [54] (https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.8b06998), Copyright (2019) American Chemical Society, further permissions related to the material excerpted should be directed to the ACS.