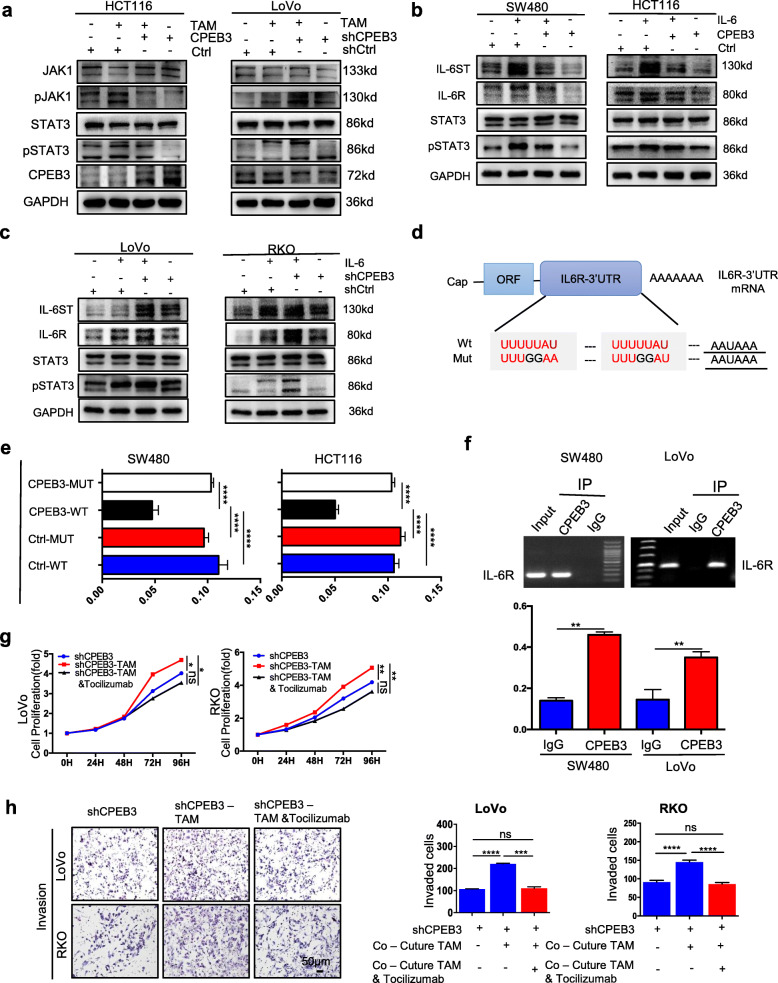
Fig. 4.
CPEB3 inhibits IL-6R/STAT3 signaling via direct binding to IL-6R mRNA in CRC cells (a) The effect of the TAMs on the JAK1, pJAK1, pSTAT3, and STAT3 in CRC cells (HCT116-Ctrl/CPEB3 and LoVo-shCtrl/shCPEB3) was analyzed by western blot analysis. (b) The effect of IL-6 on the IL-6ST, IL-6R, STAT3, and pSTAT3 in CRC cells (SW480-Ctrl/CPEB3 and HCT116-Ctrl/CPEB3) was analyzed by western blot analysis. (c) The effect of IL-6 on the IL-6ST, IL-6R, STAT3, and pSTAT3 in CRC cells (LoVo-shCtrl/shCPEB3 and RKO-shCtrl/shCPEB3) was analyzed by western blot analysis. (d) Schematic diagram of IL-6R-3′ -UTR reporter mRNA. (e) Luciferase assays were performed to detect the binding activity of CPEB3 and IL-6R. Relative fold-change in luciferase activity is shown; error bars, SEM. (f) RT-PCR of the RIP products confirmed the direct binding capacity of CPEB3 to the IL-6R-3′ -UTR in SW480 and LoVo cells. qRT-PCR of the RIP products further confirmed the direct binding capacity of CPEB3 to the IL-6-3′-UTR in SW480 and LoVo cells. Input, 5% of total lysate; error bars, SEM. (g) Cell Counting Kit-8 was used to quantify the number of LoVo/RKO-shCPEB3 cells, cultured TAMs supernatants, and TAMs supernatants treated with tocilizumab (5 ng/mL). (h) The invasion of LoVo/RKO-shCPEB3 and LoVo/RKO-shCPEB3 co-cultured TAMs treated with or without tocilizumab (5 ng/mL) was measured by a Transwell assay (200× magnification); error bars, SEM. ns, not significant; * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001; **** P < 0.0001