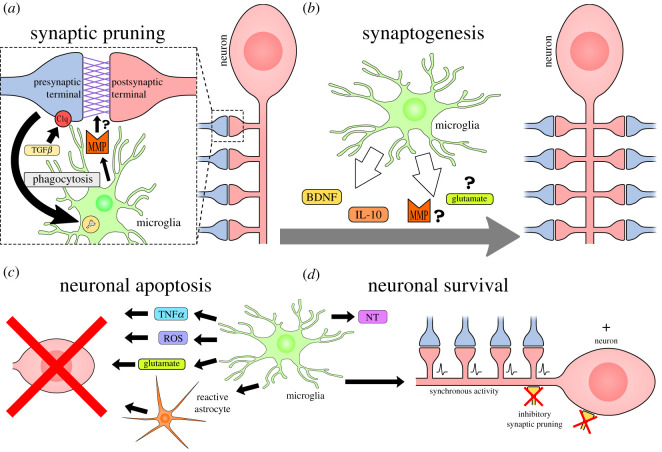
Figure 1.
Microglial sculpting mechanisms. Microglia constantly survey their local environment, and have been shown to contribute to the following structural changes in the central nervous system. (a) Synaptic pruning can be driven by C1q tagging of synapses, which promotes the phagocytosis of presynaptic terminals. TGFβ promotes C1q expression for this tagging process. Synaptic removal may rely on protease activity by microglia to break down synaptic adhesion molecules. (b) Microglia secrete factors including BDNF, IL-10 and potentially MMP and glutamate to promote synaptogenesis. Adhesion molecule binding (NCAM, integrin) may also promote synapse formation. (c) Microglia drive neuronal cell death through secretion of ROS, TNFα, glutamate and induction of reactive astrocytes. (d) Microglia promote neuronal survival through the provision of neurotrophic factors and growth factors (NT) and can promote synchronous synaptic activity through inhibitory synapse pruning which promotes survival pathways.