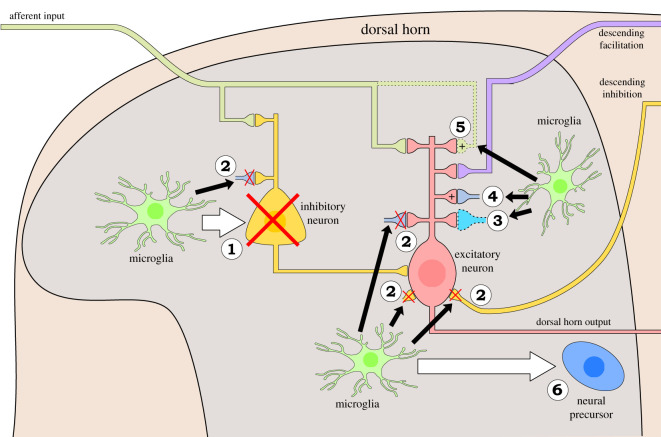
Figure 2.
Schematic of microglial sculpting of pain pathway (1–6). Peripheral afferents synapse in the dorsal horn onto the pain pathway where they are modulated by interneurons, descending fibres from the brain (descending facilitatory and inhibitory influences), microglia and astrocytes after injury. We propose that microglia mediate structural remodelling of excitatory and inhibitory neurons of the pain pathway through six different mechanisms illustrated here. (1) Inhibitory cell death: death of interneurons (shown by a red cross) in the dorsal horn reduces inhibitory gating on pain transmission. (2) Synaptic pruning: pruning of synapses (indicated with red crosses) can alter the excitatory/inhibitory balance in the dorsal horn. (3) Synaptic remodelling: alterations in synaptic proteins may promote disinhibition of ascending fibres mediating pain transmission and mediate integration of immature neurons into dorsal horn circuitry. (4) Dendritic spine remodelling: increases in spine density promotes hyperexcitability. (5) Survival and ectopic sprouting: survival and sprouting of excitatory afferents and descending neurons may promote hyperexcitability and alterations in connectivity. (6) Neurogenesis: increased neurogenesis may remodel neural circuitry in the dorsal horn and mediate pain memory.