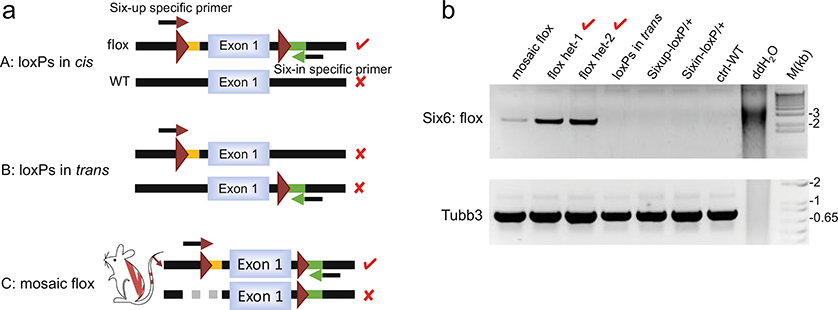
Fig. 6.
Identification of the floxed (cis-loxP sites) allele. (a) Schematic diagram of allele-specific PCR strategy to amplify DNA strand with two loxP sites integrated in cis configuration. Mouse C shows a founder mouse carrying a mosaic flox allele that does not have germline transmission. Arrow with maroon arrowhead: a forward primer with 3′ terminus complementary to the upstream loxP site; arrow with green arrowhead: a reverse primer with 3′ terminus complementary to the downstream loxP-linked restriction site. Red check mark: successful PCR amplification resulted from annealing of both primers to the DNA molecule. Red cross mark: no amplification as no primer or only one primer anneals to DNA. (b) Upper panel: representative allele-specific PCR analysis for the Six6 flox allele, with an upstream loxP-specific forward primer (Sixup-lxpF) and a downstream loxP site-specific reverse primer (Sixin-BIR) for amplification of the 2.4 Kb loxP-floxed region. Lower panel: PCR amplification of the Tubb3 gene, which serves as a control for PCR reaction