FIGURE 4.
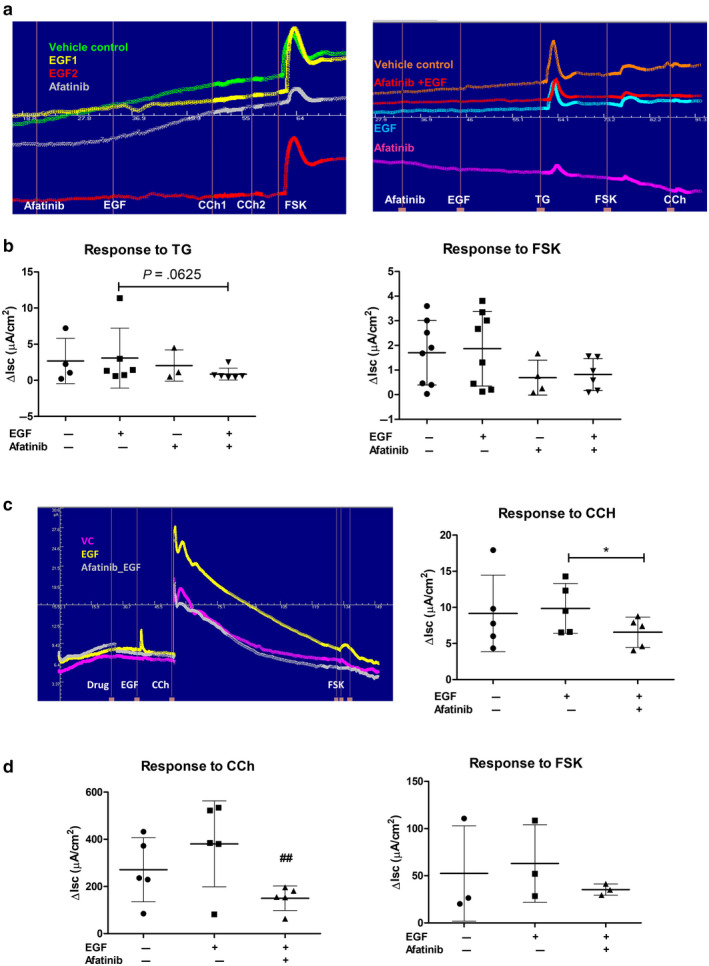
Effect of afatinib on calcium‐ and cAMP‐dependent chloride secretory responses in murine and human enteroid‐derived monolayers (EDMs). Panel a: Representative traces of Isc responses of murine colonic EDMs to carbachol (CCh), forskolin (FSK), and thapsigargin (TG) in the presence of EGF, afatinib, or both. Panel b: summary of Isc responses of murine colonic EDM to TG and FSK. Data are means ± SD superimposed and statistically analyze using Wilcoxon matched pairs signed rank test. VC, Vehicle control; A, afatinib; A + E, afatinib followed by EGF. Panel c: representative Isc responses of human EDMs to CCh and FSK in the presence of EGF, afatinib, or both. Summary data of five experiments on right show that EGF potentiated Ca2+‐dependent Cl‐ secretion in human EDM and this effect was reversed by afatinib (*p < .05) Panel d: afatinib also reversed chronic upregulation of calcium‐dependent chloride secretion induced in T84 cell monolayers exposed to EGF 24 hr prior to mounting in Ussing chambers. Data are individual values with means ± SD superimposed and statistically analyzed using repeated measures ANOVA with a Tukey post hoc test; ##p < .01, compared to response in EGF‐treated cells
