Fig. 4. Ret+ and TrkB+ Meissner afferents exhibit distinct physiological response properties.
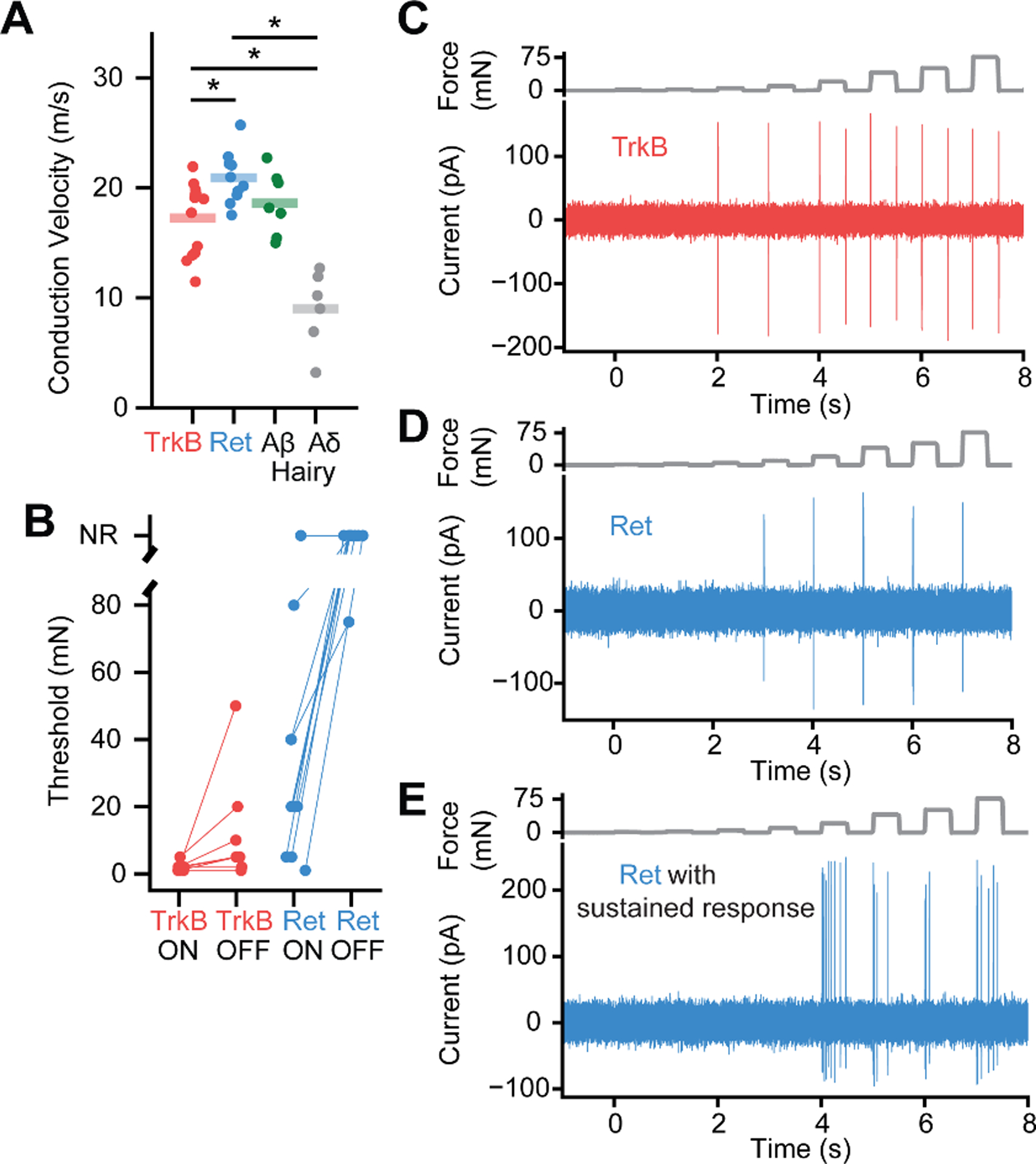
A. Both Meissner afferent subtypes have conduction velocities in the Aβ range as defined by the range of conduction velocities measured from hairy skin Aδ and Aβ LTMRs in the same preparation. The average conduction velocities for TrkB+ and Ret+ Meissner afferents are significantly different (10 afferents per type; mean ± s.e.m.: TrkB = 17.3 ± 0.9 m/s, Ret = 20.9 ± 0.8; Mann-Whitney U Test (U = 26.0, p = 0.008). * p < 0.05. B. The minimal force required to produce an action potential at the onset or offset of a step indentation for TrkB+ and Ret+ Meissner afferents. C. Response of a TrkB+ Meissner Aβ LTMR to a series of step indentations increasing in intensity from 1 to 75 mN. D. Response of a RA Ret+ Meissner afferent to the same stimuli as in C. E. Response of a SA Ret+ Meissner afferent.
