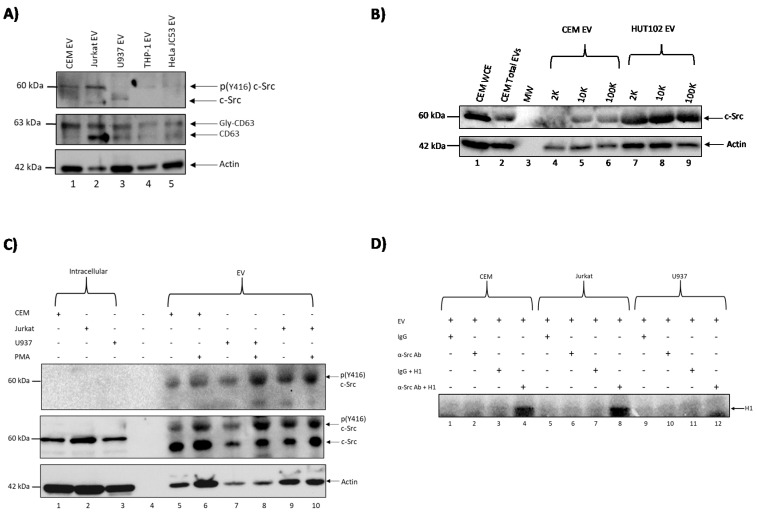
Figure 1.
c-Src is present in extracellular vesicles (EVs) in different cell lines and EV populations. (A) One milliliter of cell supernatant from CEM, Jurkat, U937, THP-1, and HeLa JC53 cells was collected and treated with Nanotraps (NT80/82) prior to rotating for 72 h at 4 °C to concentrate EVs. EVs were then Western blotted for the presence of c-Src and CD63 (exosomal marker). Actin was used as a loading control. (B) 2K, 10K, and 100K EV populations were isolated from CEM and HUT102 cells via ultracentrifugation and Western blotted for c-Src. CEM whole cell extracts (WCEs) and CEM total EVs (comprising of 2K, 10K, and 100K EV populations) were used as positive controls, while actin served as a loading control. (C) CEM, Jurkat, and U937 cells were treated with 100 nM phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and allowed to incubate for five days at 37°C with a second PMA treatment on Day 3. EVs were then concentrated using NT80/82 and rotated overnight at 4°C. Samples were Western blotted for c-Src and actin. WCEs were used as positive controls for Western blots. Actin was used as a loading control. (D) CEM, Jurkat, and U937 EVs were collected, lysed, and immunoprecipitated (IP) overnight with antibodies against IgG and c-Src. Complexes were then precipitated with protein A+G agarose beads for 2 h at 4 °C. IPs were washed twice with TNE (Tris (pH7.5), NaCl, EDTA) buffer and kinase buffer prior to incubation with γ-32P ATP. The IPs were then used for in vitro kinase assays using histone H1 as a substrate.