Figure 3. GABAergic RVM Neurons Control the Excitability of Spinal Enkephalinergic Neurons.
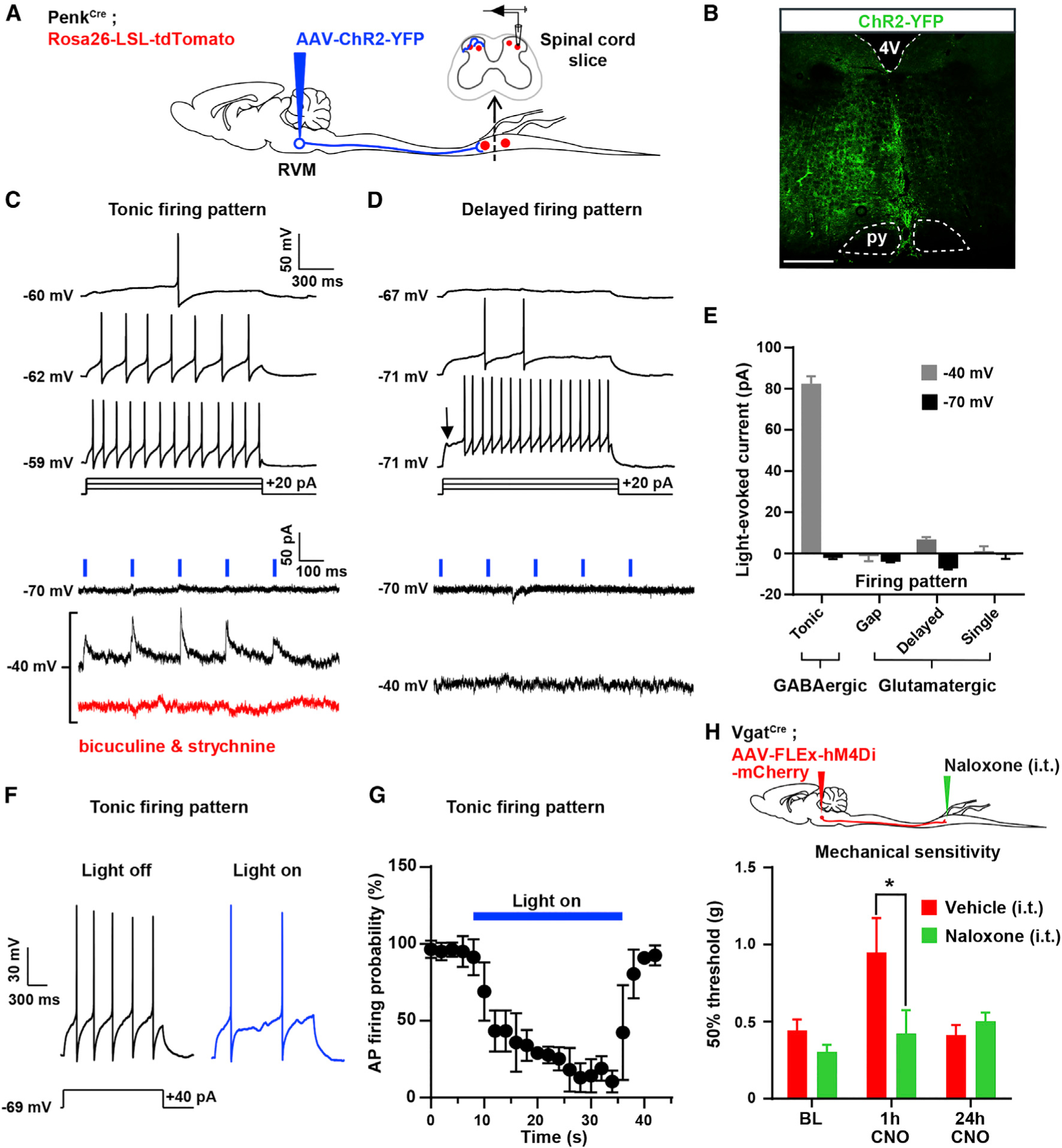
(A) Experimental approach used to test the functional connectivity between RVM neurons and Penk+ spinal neurons. An AAV was injected into the RVM of PenkCre;Rosa26-LSL-tdTomato mice to express ChR2-YFP in RVM neurons. Recordings from tdTomato+ neurons in spinal cord slices were performed during optogenetic stimulation of ChR2-YFP+ axons of RVM descending neurons.
(B) Expression of ChR2-YFP in the RVM.
(C) 5 Hz blue light pulses induced robust positive inward (inhibitory) currents at −40 mV without failure. These currents were blocked by bath application of 10 μM bicuculline and 2 μM strychnine. All neurons presenting blue light-evoked IPSCs showed a tonic action potential firing pattern, a hallmark of GABAergic spinal neurons.
(D) No EPSCs or IPSCs were evoked by light stimulation at either −70 mV or −40 mV in Penk+ neurons presenting a delayed firing pattern (glutamatergic spinal neurons).
(E) Summary graph showing the amplitude of light-evoked currents recorded in spinal Penk+ neurons presenting a tonic, gap, delayed, or single firing pattern. IPSCs were only observed in neurons with a tonic firing pattern.
(F) Light stimulation reduced action potential firing triggered by current injection in Penk+ neurons showing a tonic firing pattern.
(G) Light stimulation reduced the probability of action potential firing in Penk+ GABAergic neurons (n = 16 neurons).
(H) I.t. naloxone reversed the mechanical hyposensitivity induced by CNO in VgatCre mice injected with AAV-FLEx-hM4Di-mCherry in the RVM (two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni post hoc test, *p < 0.05, n = 12).
16 neurons were recorded for these electrophysiological experiments. Scale bar represents 500 μm. All graphs represent mean ± SEM.
