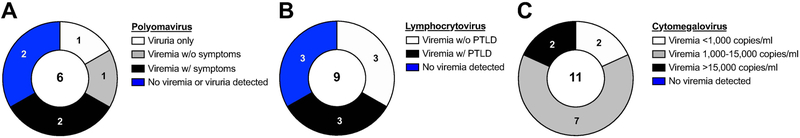
Figure 1. Frequency of viral reactivations in HSCT recipient Mauritian cynomolgus macaques.
Pie charts summarize findings among HSCT recipient macaques analyzed for A, Polyomavirus, B, Lymphocryptovirus, and C, Cytomegalovirus reactivation. Numbers on each slice correspond to the number of macaques belonging to each group as described in the corresponding legend. Numbers in the middle of each chart represent the number of recipients analyzed. Viremia and viruria were defined as >60 copies/ml plasma or urine, the limit of detection for quantitative PCR assays. Polyomavirus symptoms include hematuria, hemorrhagic cystitis, and/or kidney dysfunction, defined as a serum blood urea nitrogen and/or creatinine levels exceeding the normal range of 10 to 21 and 0.6 to 1.3 milligrams per deciliter, respectively. Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD) was diagnosed by tissue histology.