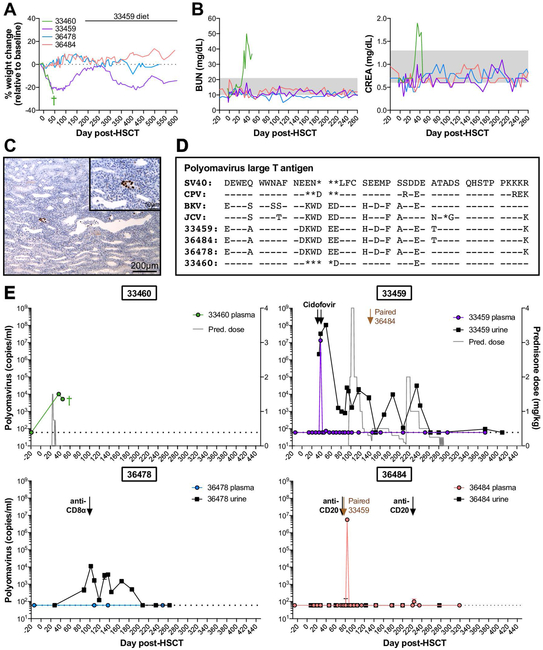
Figure 2. Polyomavirus reactivation varies among HSCT recipient macaques and can result in hemorrhagic cystitis and nephropathy.
A, Weight changes in four HSCT recipient macaques with detectable polyomavirus. B, Longitudinal blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine (CREA) in serum of HSCT recipient macaques shown in part A. Gray boxes indicated the normal ranges. C, SV40 T antigen immunohistochemistry of 33460 kidney at time of euthanasia. Main (10X magnification): Multifocally, nuclei within infected epithelial cells are immunoreactive to SV40 T antigen. Inset (40X magnification): Infected renal tubular cells exhibit nuclear positivity. D, Amino acid sequence alignment of large T antigens from human polyomaviruses (BK, JC), previously identified macaque polyomaviruses (SV40, CPV), and polyomaviruses from HSCT recipient macaques shown in part A. Sequences shown correspond to amino acids 89 to 131 of SV40 large T antigen. Genbank accession numbers for SV40, CPV, BK virus Dunlop strain, and JC virus are provided in Materials & Methods section. Dashes indicate identical amino acids; asterisks indicate deletions. E, Longitudinal Polyomavirus viral loads in plasma (colored circles) and urine (black squares) of HSCT recipient macaques shown in part A, measured by quantitative PCR. Undetectable viral loads are graphed as 60 DNA copies/ml, the limit of detection for the assay, indicated by horizontal dotted lines. Based on sequence variation among detected Polyomavirus amplicons (see part E), a distinct probe sequence was required for quantitative PCR of 33460, described in Materials & Methods section. Arrows indicate intravenous cidofovir for treatment of CMV reactivation. Gray trace on 33460 and 33459 graphs indicates daily doses of oral prednisone (pred.). Labeled black arrows indicate treatment with depleting antibodies targeted CD20 and CD8α. Labeled brown arrows indicate timepoint 33459 and 36484 were paired. Green cross indicates timepoint of 33460 euthanasia.