Fig. 7.
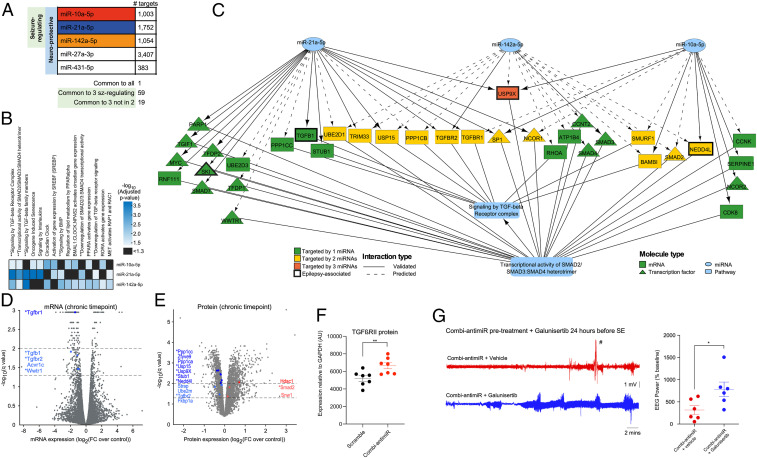
Target identification and pathway enrichment analysis identified TGF-β signaling as a potential convergent mechanism of the seizure-modifying miRNAs. (A) Number of mRNAs targeted by each miRNA. One mRNA (thyroid hormone receptor beta) is targeted by all 5 miRNAs. A total of 59 mRNAs are targeted by the 3 seizure-modifying miRNAs, 19 of which are not targeted by either miR-27a-3p or miR-431 (SI Appendix, Table S3). All targets are listed in Dataset S2. (B) Significantly enriched Reactome pathways for each of the seizure-modifying miRNAs. ** indicates pathways associated with TGF-β signaling. (C) Wiring diagram depicting mRNA targets of the 3 seizure-modifying miRNAs that are involved in the Reactome pathways: signaling by TGF-beta receptor complex and transcriptional activity of SMAD2/SMAD3:SMAD4 heterotrimer, illustrating the convergence of diverse miRNA targets at the pathway level. (D) mRNA expression levels (normalized to control) of rat hippocampi isolated at the chronic time point of the PPS model. mRNAs above the dashed lines (drawn at −log10[q value] = 1.3 and 2.0) were considered statistically significant. Fold changes are shown on the x axis with significantly dysregulated mRNAs involved in the TGF-β signaling pathways highlighted in blue (all down-regulated). * denotes mRNAs which are targeted by miR-10a-5p, miR-21-5p, and/or miR-142-5p, as depicted in C. (E) Protein expression levels (normalized to control) of rat hippocampi isolated at the chronic time point of the PPS model. Proteins above the dashed lines (drawn at −log10[q value] = 1.3 and 2.0) are considered statistically significant. Fold changes are shown on the x axis with proteins involved in the TGF-β signaling pathways are highlighted in blue (down-regulation) and red (up-regulation). * denotes proteins which are targeted by miR-10a-5p, miR-21-5p, and/or miR-142-5p, as depicted in C. (F) Graph showing semiquantification of Western blot analysis of mouse brains taken 24 h after IAKA-induced SE shows that pretreament with combi-antimiR derepresses TGFβRII expression. Brain tissue samples were from mice in Fig. 6B, where combi-antimiR pretreatment reduced SE. (G) Coadministration of the TGF-β pathway inhibitor galunisertib occludes the antiseizure effect of combi-antimiR. (Left) Raw EEG traces show SE induced by IAKA in mice pretreated with combi-antimiR and galunisertib (blue trace) or vehicle control (red trace). (Right) TGF-β pathway inhibition with galunisertib blocks the antiseizure effects of combi-antimiR pretreatment (#, EEG artifact [excluded from analysis], n = 6 mice per group, t test *P < 0.05).