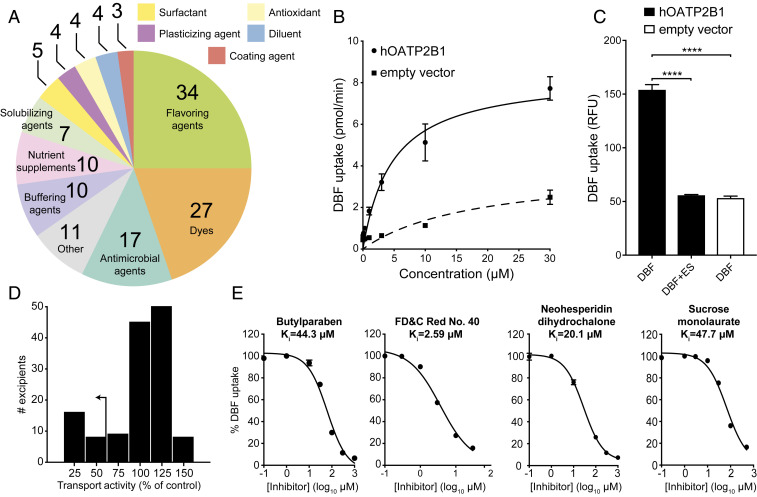
Fig. 1.
Multiple oral excipients inhibit OATP2B1-mediated transport. (A) Functional categories of the 136 oral molecular excipients included in our screen. (B) Kinetics of human OATP2B1-mediated DBF uptake. Human OATP2B1-overexpressing (circles) and empty vector-transfected HEK cells (squares) were incubated with DBF from 0.01 μM to 30 μM for 2 min. Data points represent the mean ± SD of DBF uptake from three or more replicate determinations in three experiments. (C) Human OATP2B1-overexpressing HEK cells (black bars) were incubated in HBSS uptake buffer containing 2 μM DBF for 3 min with or without 200 μM estrone sulfate (ES). Empty vector-transfected HEK cells (white bar) were assayed as above for background DBF uptake determination. Each column represents the mean ± SD of DBF uptake from eight replicate determinations. ****P < 0.0001, ANOVA with Dunnett’s correction. (D) Histogram showing the inhibition results of screening 136 excipients against OATP2B1 uptake. Our <50% transport activity cutoff is indicated by the arrow. (E) Dose–response curves of excipients against OATP2B1 transport. A representative excipient from each functional category is shown. Values represent the mean ± SD of DBF uptake from three replicate determinations in a single experiment.