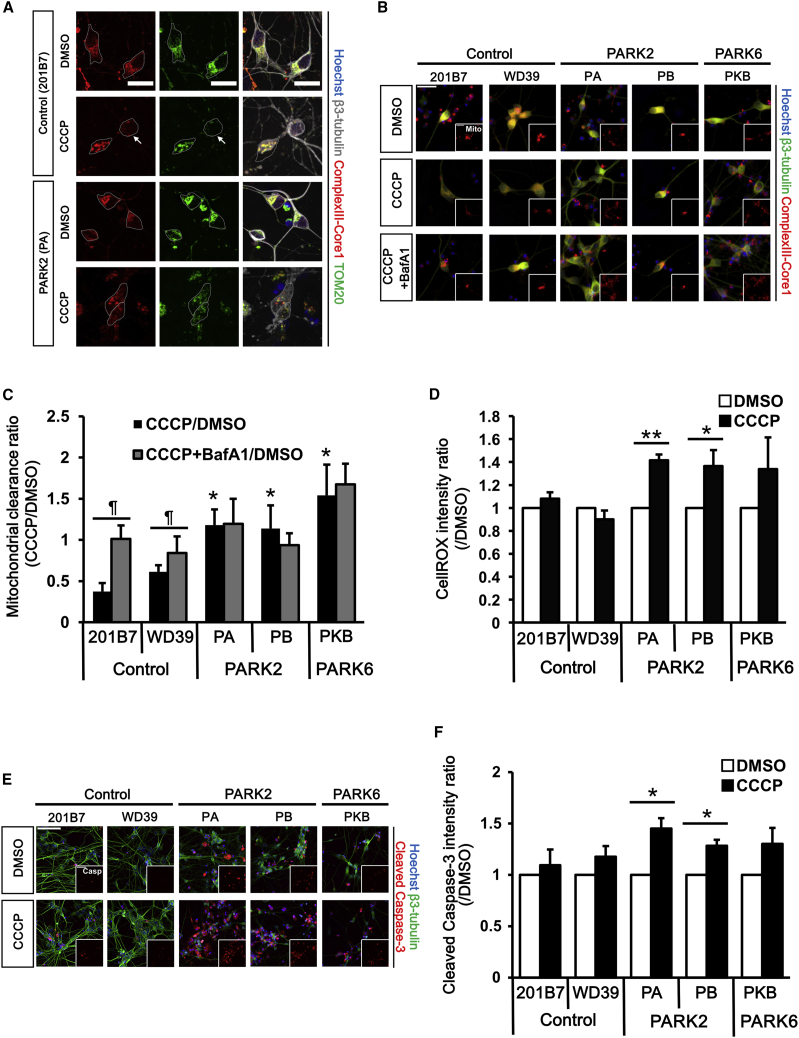
Figure 1.
Establishment of a High-Throughput Phenotype Detection System
(A) Immunostaining of control and PARK2 neurons with antibodies against mitochondrial proteins (ComplexⅢ-Core1 and TOM20) and a neuronal marker (β3-tubulin). Gray dotted lines indicate neuron cell bodies. Mitochondria are eliminated in the CCCP-treated control neuron (arrows). Scale bar, 20 μm.
(B) Representative images of the mitochondrial clearance assay. Scale bar, 20 μm.
(C) Quantitative data of the mitochondrial clearance assay. The mitochondrial area was reduced in day 32 control neurons treated with CCCP but not in day 32 PARK2 (PA and PB) and PARK6 (PKB) neurons. Data represent the ratio of mitochondrial area in neurons treated with CCCP (30 μM)/BafA1 (5 μM) and that in neurons treated with DMSO (n = 4 independent replicates; mean ± SEM). ∗p < 0.05 compared with 201B7, ¶p < 0.05 compared between CCCP treatment and CCCP + BafA1 treatment by Wilcoxon rank sum test.
(D) ROS accumulation assay. Data represent the ratio of fluorescent intensity of day 32 CCCP-treated neurons and that of DMSO-treated neurons (n = 5 independent replicates; mean ± SEM). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 compared with DMSO by Wilcoxon rank sum test.
(E) Representative images of the cell-viability assay. Scale bar, 100 μm.
(F) Quantitative data of the cell-viability assay. Data represent the ratio of fluorescence intensity of cleaved caspase-3 in day 32 CCCP-treated neurons and that in day 32 DMSO-treated neurons (n = 5 independent replicates; mean ± SEM). ∗p < 0.05 compared with DMSO by Wilcoxon rank sum test.
BafA1, bafilomycin A1; CCCP, carbonyl cyanide 3-chlorophenylhydrazone. See also Figure S1.