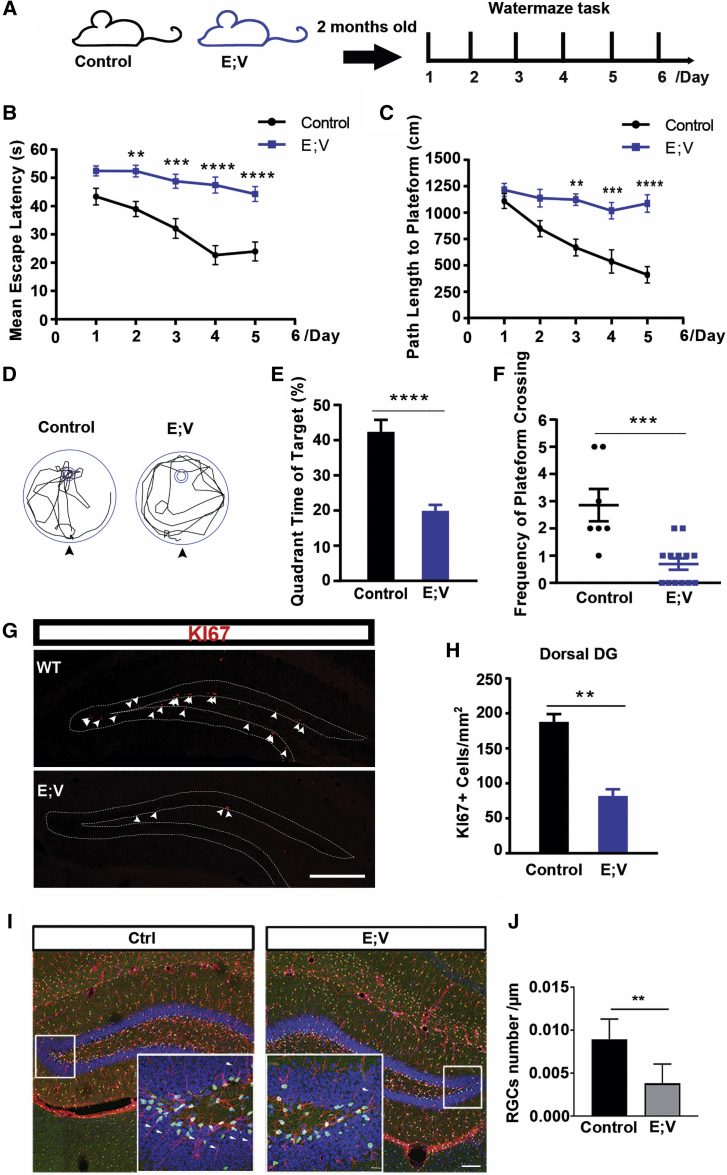
Figure 6.
Loss of VCAM1 Embryonically Impairs Spatial Learning and Memory Behavior and Reduces Adult NSCs
(A) Experimental design of the Morris water maze task for EMX-Cre; VCAM1fl/fl (E; V) and their littermate control (Control) mice, including EMX-Cre; VCAM1+/+, EMX-Cre; VCAM1fl/+ and VCAM1fl/fl mice at 2 months old.
(B and C) Quantification analysis of the escape latency (B) and path length to the platform (C) at each training day of acquiring trials between adult E; V and control mice.
(D) Representative swim paths during probe trial of adult E; V and control mice. The annulus stands for the position of removed hidden platform. Arrowheads indicate a start location.
(E and F) Quantitative analysis of the percentage of the time spent in the target quadrant (E) and the frequency of crossing the hidden platform (F) between adult E; V and control mice during probe trial.
(G and H) Representative images (G) and quantitative analysis (H) of Ki67 staining (red) in the dorsal DG between adult E; V and control mice. Arrowheads indicate Ki67+ signals along the SGZ. (I–J) Representative images (I) and quantitative analysis (J) of the radial process penetrating the whole GCL in SOX2+ GFAP+ stained (red) cells in dorsal DG between adult E; V and control mice. Arrowheads indicate radial processes of NSCs (SOX2+ GFAP+) along the SGZ.
Scale bars: (G and I) 250 μm and 12 μm (inset). Data represent mean ± SEM. (B, C, E, and F) E; V, 13 mice; control, 7 mice; (H and J) E; V, 4 mice; control, 3 mice. Two-way ANOVA for (B) and (C); Student's t test for (E), (F), (H), and (J). ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.