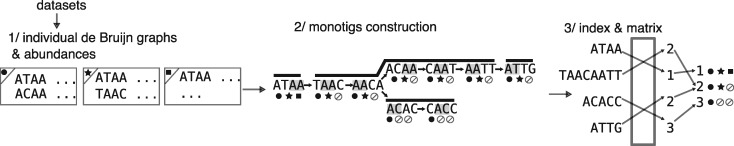
Fig. 3.
Overview of REINDEER index construction. At step 1/, for each dataset, the (compacted) de Bruijn graph is given as input along with the count of each unitig. At step 2/, monotigs (corresponding to paths in dark grey) are computed on the k-mers of the union de Bruijn graph of all datasets, and these monotigs are indexed. During step 3/each monotig is associated (through an integer array) to a row in the de-duplicated count-vector matrix (rightmost matrix). In this matrix no two rows are equal, and in practice each row is compressed