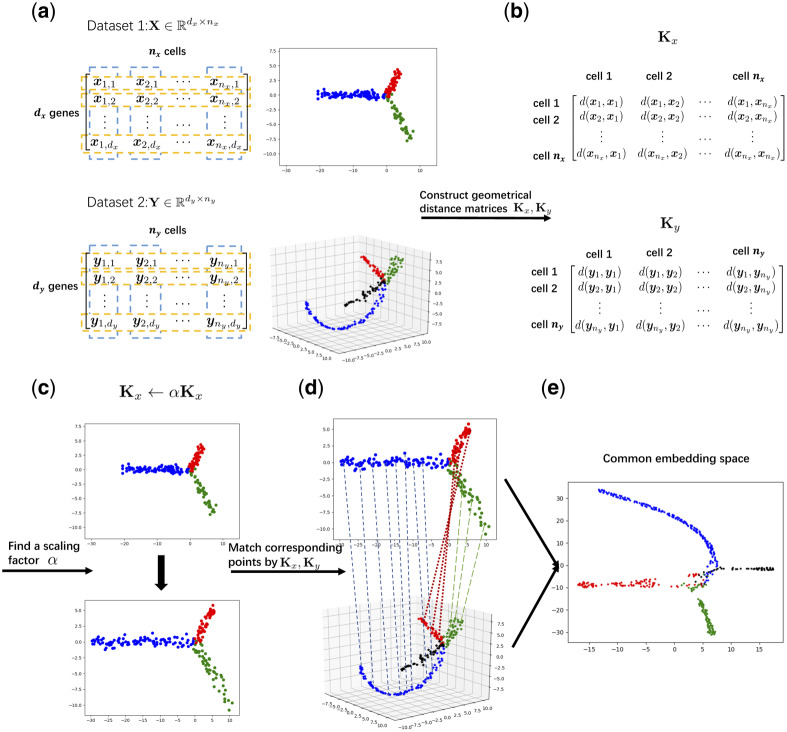
Fig. 1.
Schematic overview of UnionCom. (a) Given the input of single-cell multi-omics datasets (e.g. Datasets 1 and 2), which have similar embedded topological structures, UnionCom (b) embeds the intrinsic low-dimensional structure of each single-cell dataset into a geometrical distance matrix of cells within the same dataset; (c) rescales the global distortions on the topological structures across datasets by a global scaling parameter α; (d) aligns the cells across single-cell datasets by matching the geometrical distance matrices based on a matrix optimization method; and (e) finally projects the distinct unmatched features across modalities into a common embedding space for feature comparability of the aligned cells. It does not require one-to-one correspondence among cells across datasets, and it can accommodate samples with dataset-specific cell types (see the branch with black points in Dataset 2 for example)