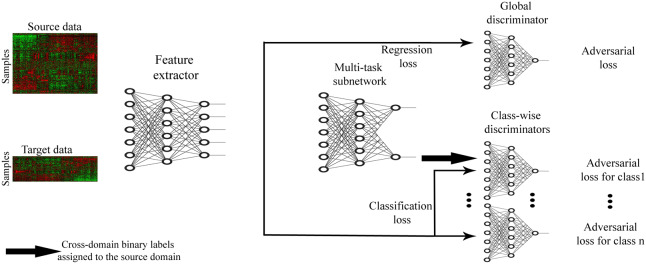
Fig. 1.
Schematic overview of AITL: first, the feature extractor receives source and target samples and maps them to a feature space in lower dimensions. Then, the multi-task subnetwork uses these features to make predictions for the source and target samples and also assigns cross-domain labels to the source samples. The multi-task subnetwork addresses the discrepancy in the output space. Finally, to address the input space discrepancy, global- and class-wise discriminators receive the extracted features and regularize the feature extractor to learn domain-invariant features. The feature extractor has one fully connected layer. The multi-task subnetwork has one fully connected shared layer followed by two fully connected layers for the regression task and one fully connected layer for the classification task. All the discriminators are single-layered fully connected subnetworks