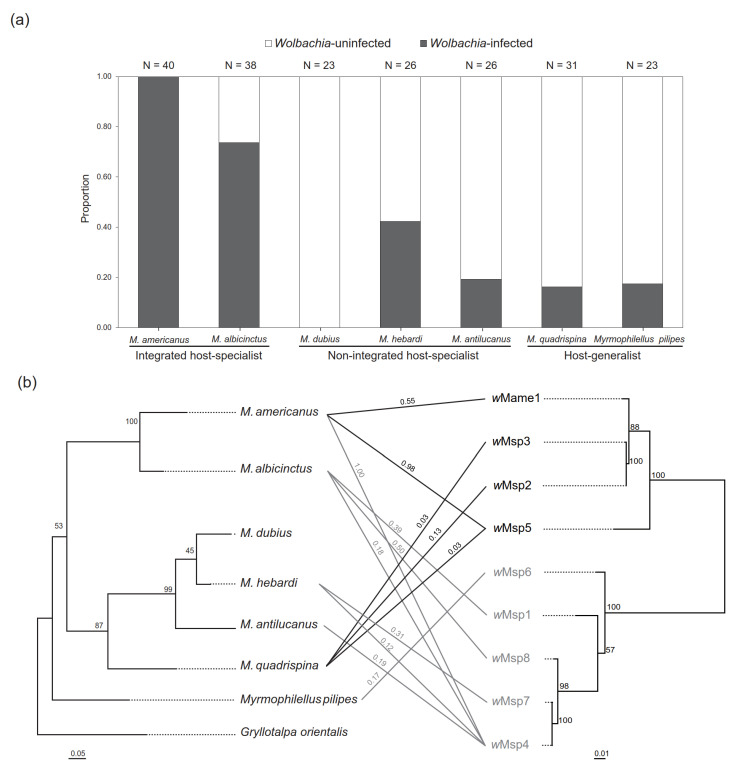
Figure 1.
(a) Wolbachia infection rates of ant crickets; (b) Maximum Likelihood (ML) phylogeny of ant crickets (left) and their corresponding Wolbachia strains (right) based on cytb sequences and concatenated sequences of wsp and MLST, respectively. Numbers at nodes indicate bootstrap support values (100 replicates). Ant cricket-Wolbachia associations are indicated by lines (black: supergroup A; gray: supergroup F), and the number above the line indicates the infection rate of each Wolbachia strain. Wolbachia strain wMame2 was excluded from the phylogenetic analysis due to the lack of reliable MLST data.