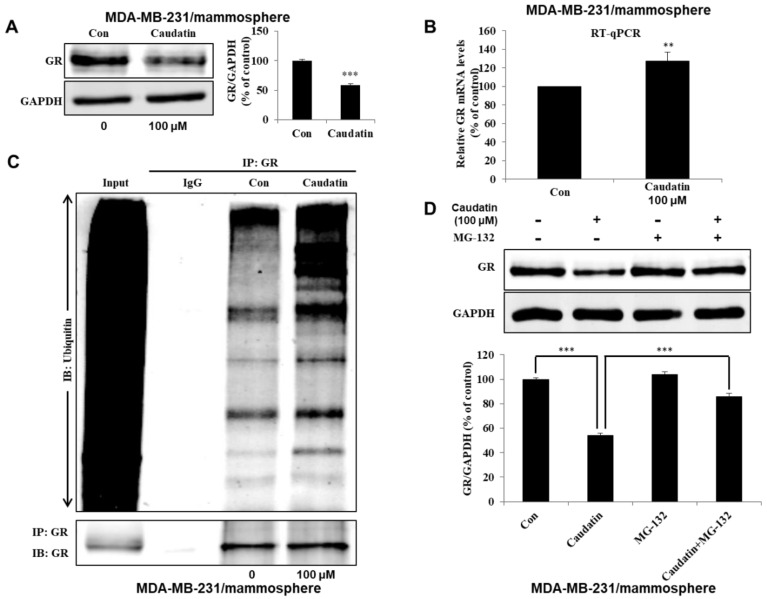
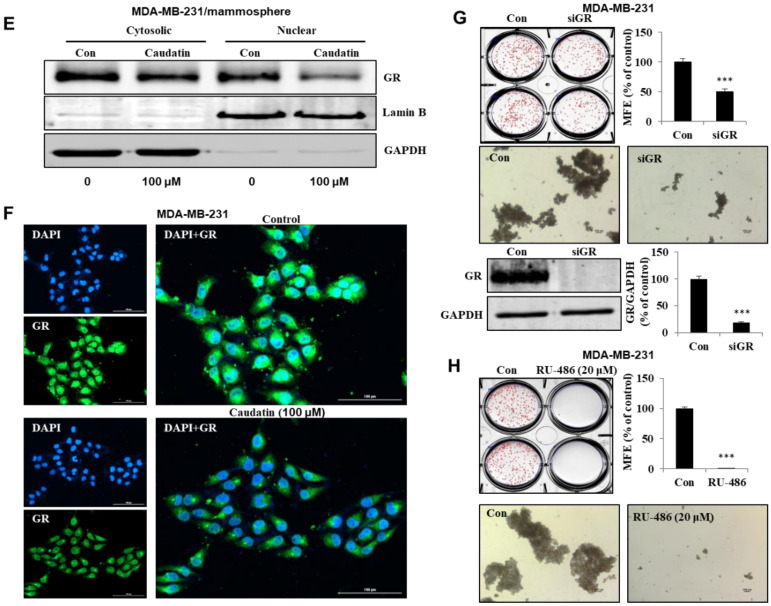
Figure 6.
Caudatin inhibits the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) signal through the ubiquitin (Ub)-dependent degradation of GR. (A) The expression level of GR in the total protein of MDA-MB-231-derived mammospheres was measured after treatment of the mammospheres with caudatin for 48 h using western blot analyses. (B) After treatment with caudatin, the transcriptional expression of the GR gene was detected in mammospheres by real-time reverse transcription- quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) using specific primers. β-actin was used as an internal control. (C) Mammospheres incubated with caudatin were lysed for immunoprecipitation (IP) with an anti-GR antibody, and western blot analysis was performed using anti-ubiquitin and anti-GR antibodies. (D) Mammospheres were incubated with caudatin and MG-132 (0.5 μM) for 24 h and lysed for western blot analysis. (E) The expression level of GR in the cytosolic and nuclear protein fractions of MDA-MB-231-derived mammospheres was measured after treatment of the mammospheres with caudatin using western blot analysis. (F) Immunofluorescence (IF) analysis of GR (green) expression and localization in MDA-MB-231 cells under caudatin treatment was performed. (G) The effect of knocking down GR expression using GR-specific siRNA on mammosphere formation was evaluated. (H) The effect of RU-486, an antagonist of GR, on mammosphere formation was evaluated. The data are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001 versus the DMSO-treated control group.