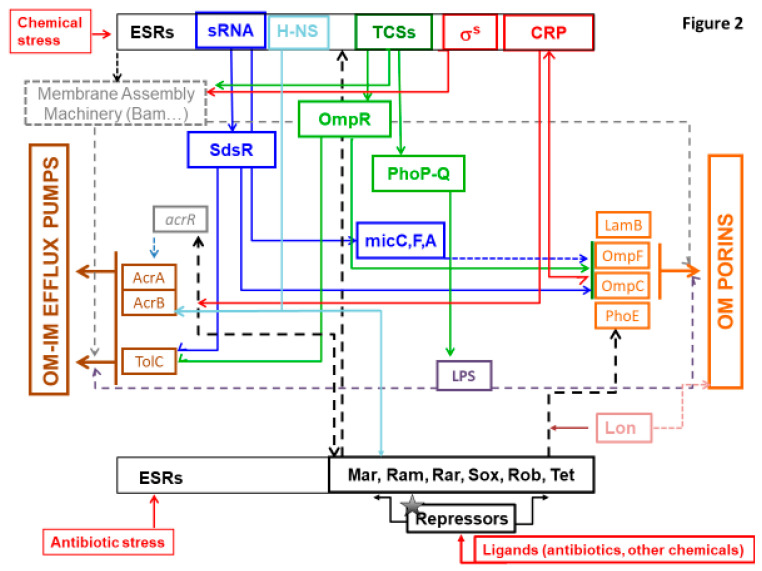
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of several bacterial effectors that control membrane permeability and the In and Out of molecules. The various regulation cascades that modulate the OM permeability including porins (orange square, on the right of the diagram), and the expression of major efflux pumps (AcrAB, OqxAB; brown square, on the left of the diagram) are illustrated. In response to external stimuli (red arrows), such as chemicals including antibiotics, Envelope Stress Response (ESR) effectors are triggered and activate multiple regulation pathways, promoting the development of MDR phenotypes in Enterobacteriaceae. Among them, the major type 1 regulators including AraC-XylS family members and Tet are shown (at the bottom of the diagram) with their corresponding repressors (in black). MarA, RamA (absent in E. coli), RarA, SoxS, and Rob activate the AcrAB-TolC expression (and OqxAB in K. pneumoniae). They also modulate the porin expression and are involved in the membrane lipid trafficking. The Lon protease (in pink) degrades RamA and MarA. Two-component systems (TCS) (in green, at the top of the diagram) are among the main ESR effectors of type 2 regulators. They regulate processes in response to chemicals and other signals of envelope defects and subsequently controls the membrane machinery (grey square), LPS integrity (purple square), and porins expression. TCS, such as PhoPQ, induce antibiotic resistance by controlling the modification of LPS and the assembly of porins. The TCS regulator OmpR (in green) modulate the expression of the major porins under an osmotic stress, promoting a resistance to B-lactams. The H-NS (in light blue) is also involved in the response to osmotic stress and regulates the expression of efflux pumps and porins in E. coli and K. aerogenes. The Sigma factor (in red) regulates genes involved in expression of membrane protein. The sRNAs (in blue) regulate (and are regulated by) the ESRs. They have multiple mRNA target and allow to mediate a rapid and efficient response. sRNAs such as MicF, MicC, MicA (in blue) are involved in the regulation of porins expression. sRNAs also mediate the regulation of efflux pump expression with, for instance, the binding of SdsR (in blue) to the TolC mRNA. The Cyclic AMP Receptor Protein (CRP, in red), one of the most important TF in E. coli, is also involved in the regulation of efflux systems and porins expression. Overall, ESR effectors regulate LPS biogenesis that is involved in the OM proteins assembly and, consequently, the function of porins and TolC (grey dashed lines).