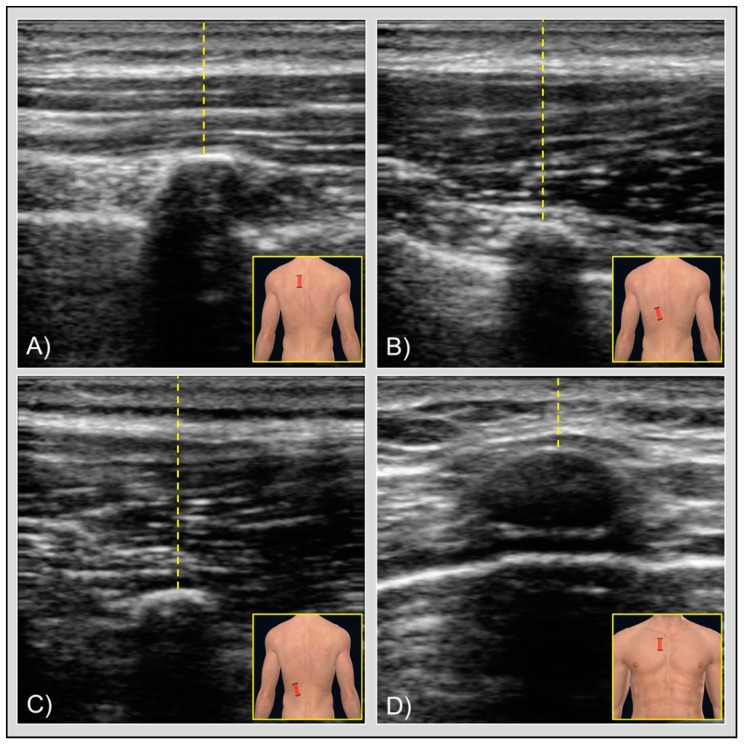
Figure 1.
Figures showing the transducer placement (brackets) with ultrasound images and skin-to-rib measurement (yellow lines) for (A) rhomboid muscle, (B) lower trapezius muscle, (C) iliocostalis muscle, and (d) pectoralis major muscle. At the center of each image, the curved hyperechoic area represents the apex of the rib. Below the bone is visible the typical hypoechoic signal, also known as acoustic shadowing. Slightly deeper, in quadrants (A,B,D), you can also notice other hyperechoic tissues lateral to the bone, which represent the pleura. In the rhomboid muscle image (A), the different muscle layers are also visible: directly above the skin the middle trapezius muscle, just below it the rhomboid muscle, and around the rib the intercostal muscles. In the pectoralis major muscle image (D), the rib apex is less visible than in the other images due to the costal cartilages.