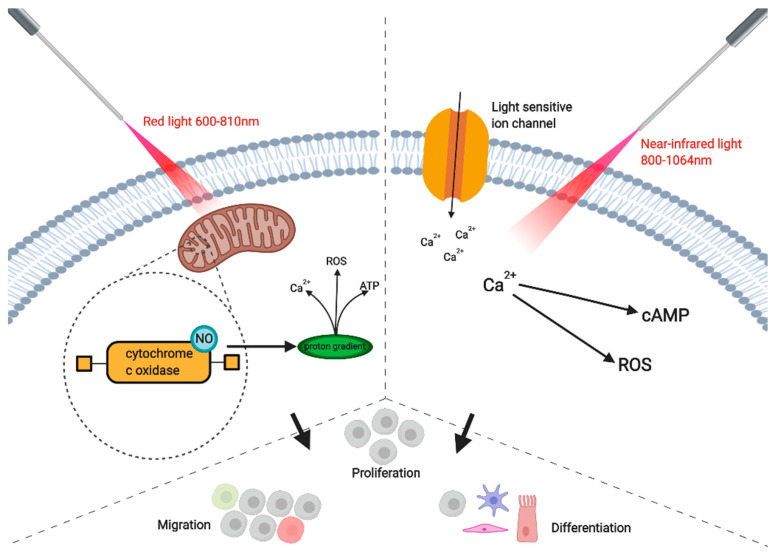
Figure 1.
The application of red light (600–810 nm) is absorbed by the enzyme cytochrome c oxidase, which is located in the unit IV respiratory chain of the mitochondria. Nitric oxide (NO) is then displaced and activates the enzyme and this leads to a proton gradient. Consequently, calcium ions (Ca2+), reactive oxygen species (ROS), and ATP production levels are increased. On the other hand, the application of near-infrared light (810–1064 nm) activates light-sensitive ion channels, and increases the levels of Ca2+. ROS and cyclic AMP (cAMP)then interact with the calcium ions. All of these activities increase cell differentiation, proliferation and migration, among other things. Created with BioRender.