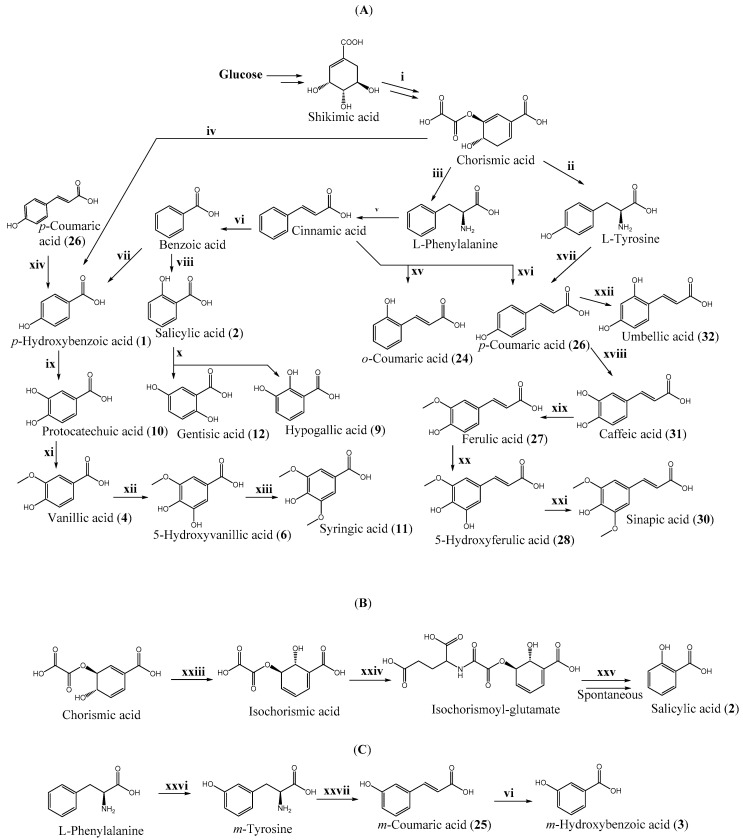
Figure 1.
General scheme for the phenolic acid biosynthesis through the shikimate pathway (A), salicylic acid biosynthesis from isochorismate (B), and m-coumaric acid biosynthesis (C). Enzymes involved in the reactions: (i) shikimate kinase, 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase and chorismate synthase; (ii) chorismate mutase, prephenate dehydrogenase; (iii) chorismate mutase, prephenate aminotransferase, arogenate dehydratase; (iv) chorismate-pyruvate lyase; (v) L-phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL); (vi) oxidase (or presumed β-oxidation); (vii) benzoic acid 4-hydroxylase; (viii) benzoic acid 2-hydroxylase; (ix) 4-hydroxybenzoic acid 3-hydroxylase; (x) salicylic acid 3-hydroxylase (S3H); (xi) protocatechuic acid 3-O-methyltransferase; (xii) vanillic acid 5-hydroxylase; (xiii) vanillic acid 5-O-methyltransferase; (xiv) 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde synthase and 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde dehydrogenase; (xv) cinnamic acid 2-hydroxylase; (xvi) cinnamic acid 4-hydroxylase; (xvii) tyrosine ammonia lyase (TAL); (xviii) p-coumaric acid 3-hydroxylase; (xix) caffeic acid 3-O-methyltransferase; (xx) ferulic acid 5-hydroxylase; (xxi) caffeic/5-hydroxyferulic acid O-methyltransferase (COMT); (xxii) p-coumaric acid 2-hydroxylase; (xxiii) isochorismate synthase (ICS); (xxiv) isochorismoyl-glutamate synthase (IGS); (xxv) isochorismoyl-glutamate A pyruvoyl-glutamate lyase (IPGL); (xxvi) cytochrome P450; (xxvii) tyrase.