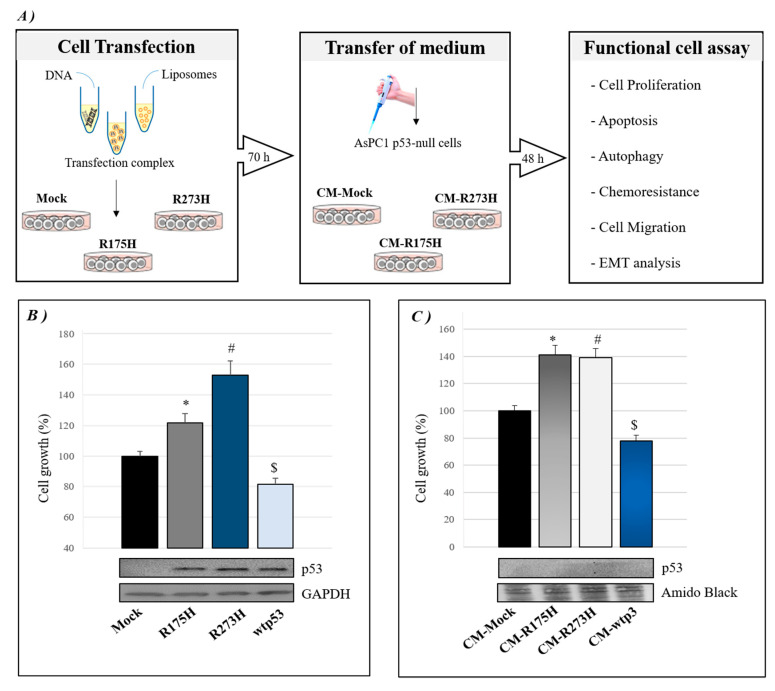
Figure 1.
Cancer cell secretome driven by mutant p53 can induce hyper-proliferative effects. (A) A summary model of the approach used in this study: p53-null AsPC-1 cells were transfected with plasmids for R273H or R175H mutant p53 over-expression or its mock vector for 48 h. Then, AsPC-1 transfected cells were washed in PBS to remove liposomes and incubated with fresh culture medium for further 22 h to accumulate secreted proteins. After that, the conditioned medium (CM) of AsPC-1 transfected cells was transferred to untransfected p53-null AsPC-1 cells. After 48 h, several biological phenomena listed in the figure were investigated in AsPC-1 cells bearing mutp53-driven CM. (B) Cell growth was measured by Cristal Violet assay in p53-null AsPC-1 cells transfected for over-expression of wtp53, R175H or R273H mutp53. Accompanying Western blotting of p53 and of GAPDH for control loading are reported. Statistical analysis * p < 0.05 R175H vs Mock; # p < 0.05 R273H vs Mock; $ p < 0.05 wtp53 vs Mock. (C) Cell growth was measured by Cristal Violet assay in untransfected p53-null AsPC-1 cells cultivated with wtp53-, R175H- or R273H-CM. Accompanying Western blotting of p53 and amido black staining are reported. Statistical analysis * p < 0.05 CM-R175H vs CM-Mock; # p < 0.05 CM-R273H vs CM-Mock; $ p < 0.05 wtp53 vs CM-Mock.