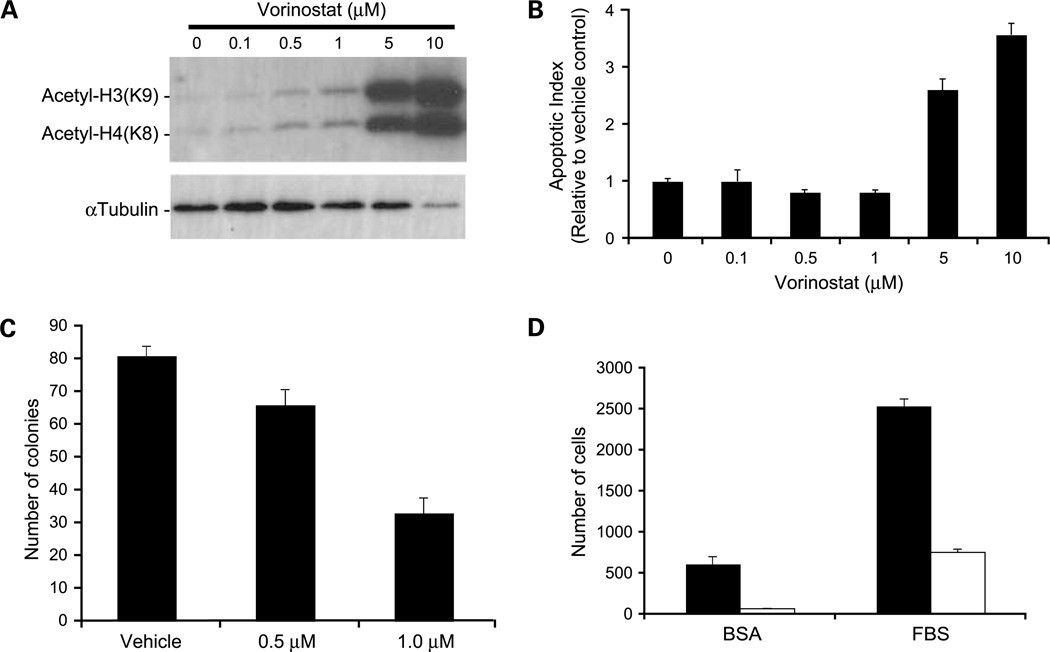
Fig. 3.
In vitro effects of vorinostat on histone acetylation and apoptosis. A, Western blot analysis of acetylated histone proteins in 231-BR cells treated with increasing concentrations of vorinostat for 24 h. B, apoptosis as measured by the Cell Death Detection ELISAPLUS (Roche). Apoptotic index determined with respect to vehicle control-treated cells given an index of 1 to account for the amount of cell death occurring naturally in a cell population. P < 0.0001, ANOVA, post-hoc Dunnett’s multiple comparison; P = 0.014 for vehicle versus 0.5 μmol/L vorinostat; P = 0.013 for vehicle versus 1 μmol/L vorinostat; P = 0.0001 for vehicle versus 5 μmol/L vorinostat; P < 0.0001 for vehicle versus 10 μmol/L vorinostat. C, clonogenic growth in response to 0.5 μmol/L (P = 0.024) and 1.0 μmol/L (P < 0.0001) vorinostat compared with vehicle control. P values were determined by two-way ANOVA with post-hoc Dunnett’s multiple comparison. D, vorinostat inhibition of cell migration as assessed by Boyden chamber motility experiments. Vorinostat inhibited both unstimulated (bovine serum albumin; P = 0.0007) and fetal bovine serum–stimulated (P < 0.0001) cell migration. P values were determined by three-way ANOVA. Black columns, vehicle control; white columns, 5 μmol/L vorinostat. Representative experiments of at least three conducted (A-D).