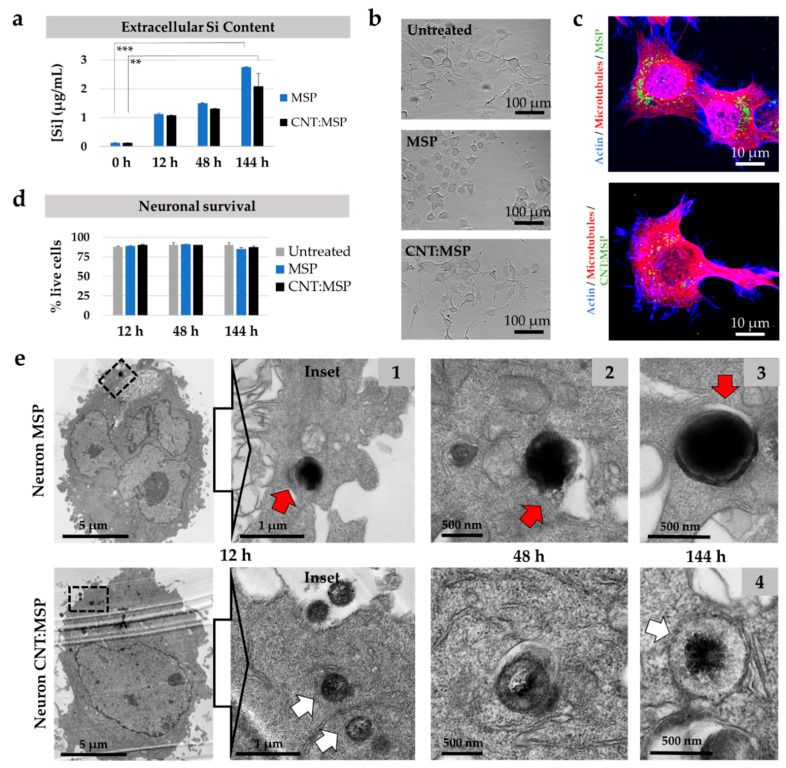
Figure 7.
Intracellular route and degradation of MSP in neurons. (a) Quantitative ICP-OES analysis of extracellular Si in cultures of NSC-34 neurons exposed to MSP and CNT:MSP. The rise of the Si species corroborates particle dissolution in these cells at the indicated times (** p < 0.025, *** p < 0.005). (b) Phase-contrast images of control neuronal cultures and cells exposed to 15 µg/mL of MSP and CNT:MSP for 6 days. No deleterious morphological changes were observed. (c) Fluorescent confocal images of neurons displaying MSP and CNT:MSP (green channel). No abnormalities in the cytoskeleton of microtubules (red channel) or actin (blue channels) were detected. (d) Neuronal survival upon exposure to the two types of particles was not affected. (e) TEM images of ultrathin sections of motor neurons containing intracellular MSP (top) and CNT:MSP (bottom). Particles reproduce the same destinies and degradation patterns described for epithelial cells. Red arrow points at the endosomal membranes surrounding a particle. White arrow shows the eroded surface of a cytosolic CNT:MSP.