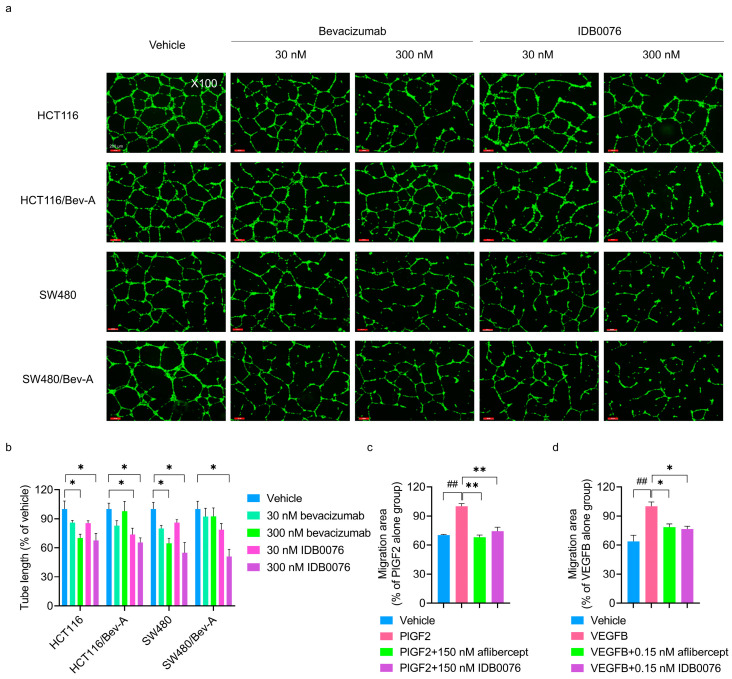
Figure 2.
IDB0076 suppresses angiogenic effects of multiple proangiogenic growth factors in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). (a,b) IDB0076 inhibited the tube formation by HUVECs stimulated by the conditioned medium (CM) derived from the parental cells (HCT116 and SW480 cells) or bevacizumab-adapted cells (HCT116/Bev-A and SW480/Bev-A cells) treated with vehicle, IDB0076, or bevacizumab for 24 h, followed by the induction of tube formation for 24 h. Representative images out of three independent experiments are shown. The results were quantified by measurement of tube length using an angiogenesis analyzer. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3); * p < 0.05 as compared with the vehicle group treated with the CM derived from each cancer cell line. Scale bars = 200 μm, ×100 magnification. (c,d) IDB0076 inhibits PlGF2- or VEGFB-induced HUVEC migration comparably to aflibercept. Under starvation, cell monolayers were scratched and treated with the indicated concentration of IDB0076 or aflibercept in the presence of either PlGF2 or VEGFB. After that, the area of migration into the scratch was determined. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3); ## p < 0.01 as compared with the vehicle group; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 as compared with the growth factor alone group.