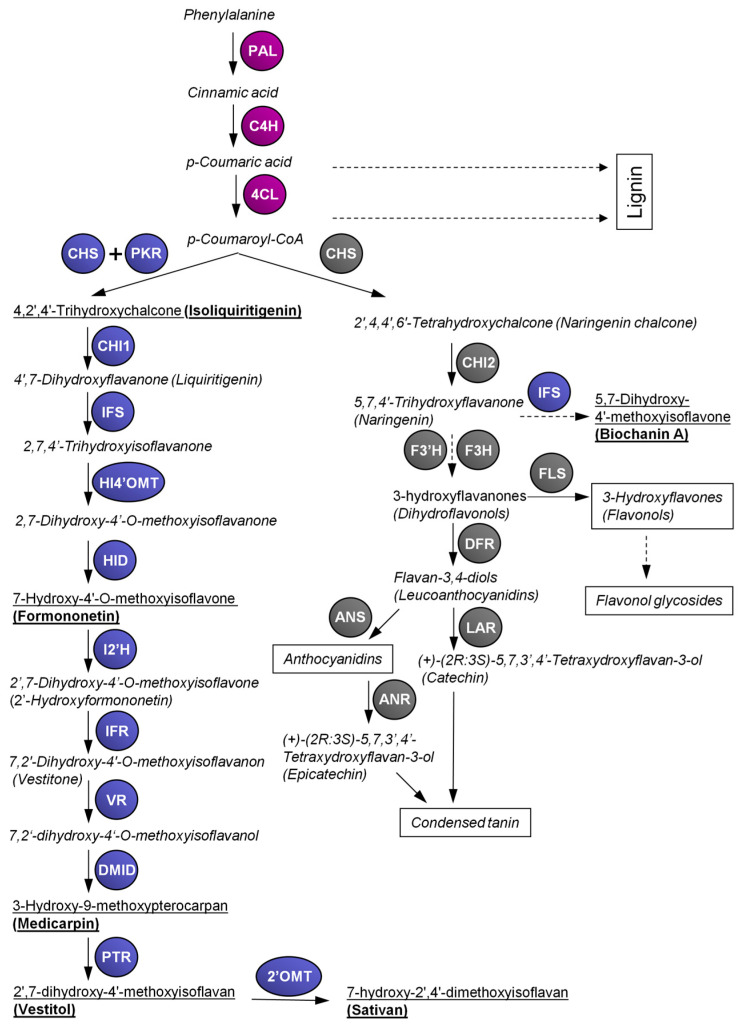
Figure 1.
Overview of the flavonoid and isoflavonoid pathways in Lotus japonicus. 4CL, 4-coumarate:CoA ligase; 2’OMT, 2’-O-methyltransferase; I2’H, isoflavone-2’-hydroxylase; ANR, anthocyanidin reductase; ANS, anthocyanidin synthase; C4H, cinnamic acid 4-hydroxylase; CHI, chalcone isomerase; DMID, 7,2’-dihydroxy-4’-O-methoxyisoflavanol dehydratase (syn. pterocarpan synthase); CHS, chalcone synthase; DFR, dihydroflavonol 4-reductase; F3H, flavanone 3-hydroxylase; F3’H, flavanone 3’-hydroxylase; FLS, flavonol synthase; HID, 2-hydroxyisoflavanone dehydratase; HI4’OMT, 2-hydroxyisoflavanone 4’-O-methyltransferase; IFR, isoflavone reductase; IFS, 2-hydroxyisoflavanone synthase; LAR, leucoanthocyanidin reductase; PAL, phenylalanine ammonia lyase; PKR, polyketide reductase (syn. chalcone reductase); PTR, pterocarpan reductase; VR, vestitone reductase. Purple color: enzymes of general phenylpropanoid pathway; grey color: enzymes of flavonoid pathway; blue color: enzymes of isoflavonoid pathway. Dashed arrows represent multiple biosynthetic steps. Trivial names of compounds are presented if they are commonly used; the others are presented by their semi-systematic names. Semi-systematic names and chemical structures of the referred flavonoids and isoflavonoids are attached online in Table S1. The names underlined in bold highlight most abundant isoflavonoids found in L. japonicus according to our data [42].