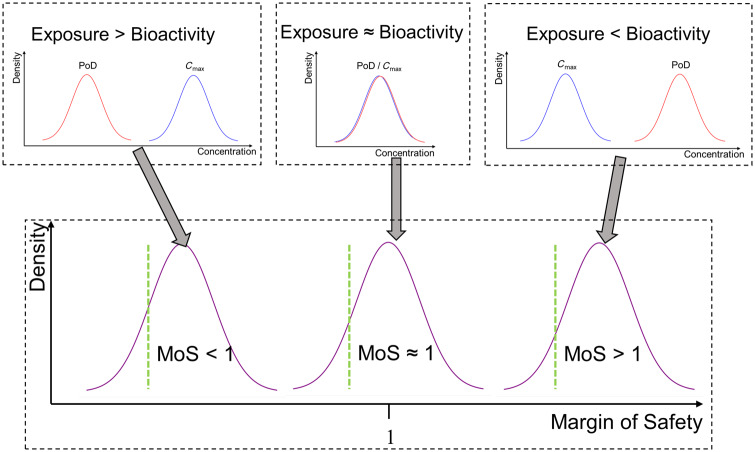
Figure 2.
C max and points of departure (PoDs) were inferred as probability distributions encompassing the uncertainty in their estimates. The margin of safety (MoS) was defined as the PoD/Cmax ratio. The uncertainty in the Cmax and PoD estimates is propagated through this calculation such that MoS estimate is also a distribution. When the distribution for the PoD is predominantly lower than the distribution for the Cmax (exposure > bioactivity), this produces a distribution for the MoS in which almost all mass is less than 1. Conversely, if the distribution for the PoD was predominantly greater than the Cmax distribution (exposure < bioactivity), almost all the mass of corresponding MoS distribution is greater than 1. When the distributions for the Cmax and PoD strongly overlap (exposure ≈ bioactivity), these results in an MoS distribution centered around 1. The location of the 5th percentile for the MoS is as illustrated on the graph (green line). For this value to be greater than 1 the PoD must, on average, be greater than the Cmax.