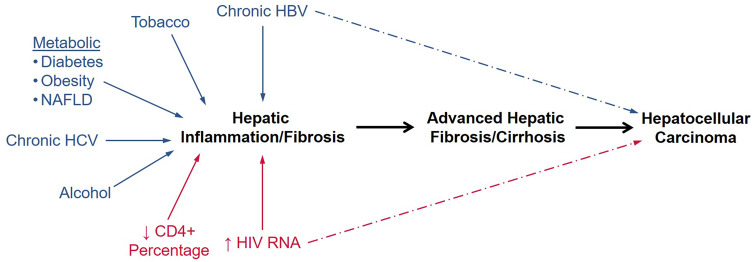
Figure 1.
Pathway to development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The figure shows the contributions of the key modifiable determinants of HCC, including traditional risk factors (blue) and the hypothesized HIV-related determinants in this study (red). Both chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and HIV viremia could increase the risk of HCC by inducing hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis or by directly promoting development of HCC outside of the liver fibrosis pathway. NAFLD = non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; RNA = ribonucleic acid.