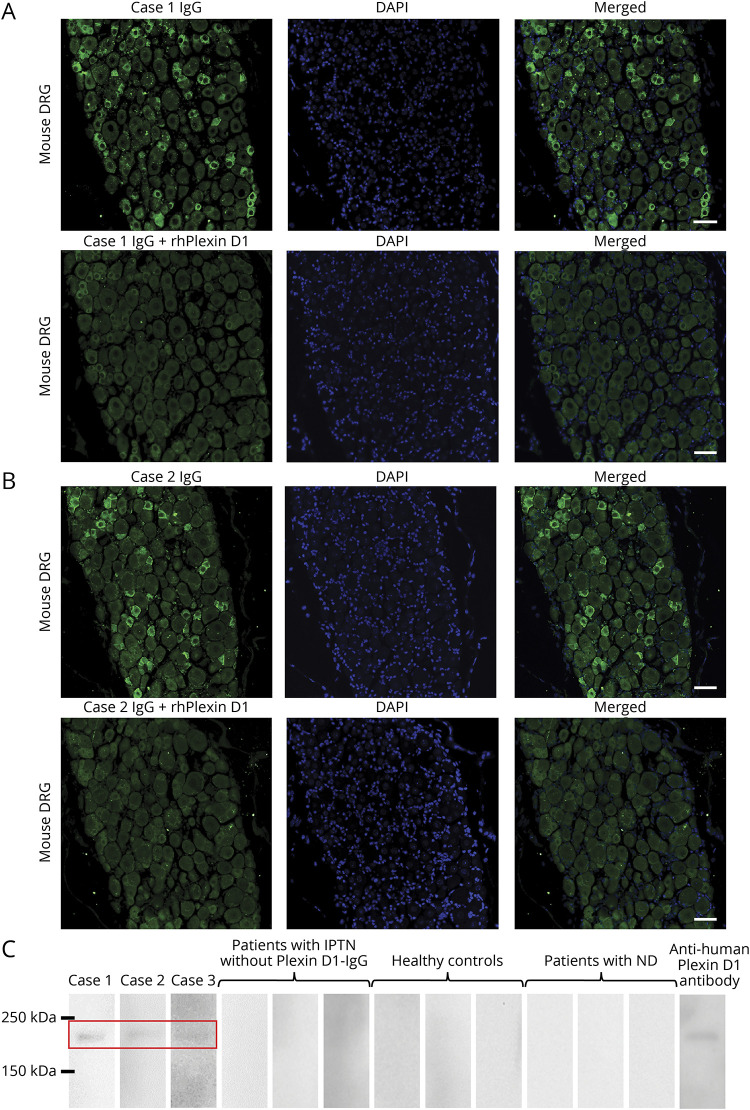
Figure 1. Detection of Plexin D1-IgG by IFA using mouse DRG and WB with rhPlexin D1.
(A) IFA with mouse DRG for case 1. IgG from case 1 (green) bound to small DRG neurons (upper images). The immunostaining (green) of small DRG neurons by IgG from case 1 was prevented by preincubation with rhPlexin D1 (2 µg/mL) (lower images). Nuclei are counterstained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue). (B) IFA with mouse DRG for case 2. IgG from case 2 (green) bound to small DRG neurons (upper images). The immunostaining (green) of small DRG neurons by IgG from case 2 was prevented by preincubation with rhPlexin D1 (2 µg/mL) (lower images). Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue). (C) WB analysis using rhPlexin D1 and IgG from cases 1, 2, and 3, 3 patients with IPTN without Plexin D1-IgG, 3 healthy controls, 3 patients with neurodegenerative diseases, and a commercial anti-human Plexin D1 antibody. WB of rhPlexin D1 with IgG samples from cases 1, 2, and 3 showed a common immunoreactive band between 150 and 250 kDa, similar to the commercial anti-human Plexin D1 antibody (R&D Systems, Minneapolis). All other samples were nonreactive. Scale bars: (A and B) = 50 µm. DRG = dorsal root ganglion; IFA = immunofluorescence assay; IPTN = idiopathic painful trigeminal neuropathy; ND = neurodegenerative diseases; Plexin D1-IgG = anti-Plexin D1 antibody; rhPlexin D1 = recombinant human Plexin D1; WB = Western blotting.