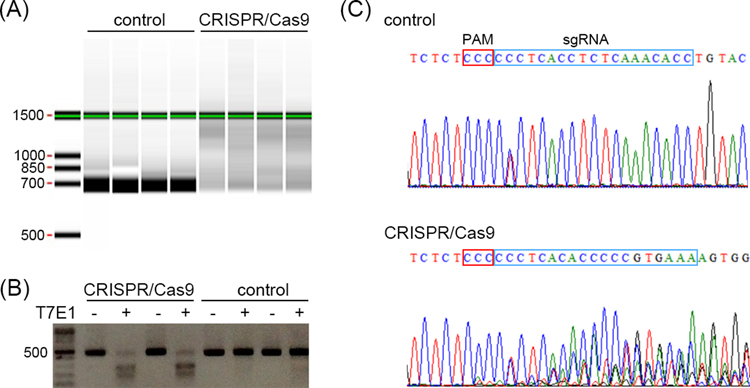
Fig. 3.
Three rapid screening methods for detecting genome editing in sea urchin embryos. (A) Rapid screening using the heteroduplex mobility assay (HMA) on a LabChip. DNA fragments from the CRISPR/Cas9 injected embryos are detected as smeared bands. (B) Rapid screening using the T7E1 assay. DNA fragments from the CRISPR/Cas9 injected embryos are cleaved into two smaller fragments. (C) Rapid screening using the Sanger sequencing. Sequencing chromatogram from the control embryo shows single peaks representing single PCR product. The only base showing two peaks may be a polymorphic site. In CRISPR/Cas9 injected embryos, multiple peaks near the cutting site are observed, indicating multiple PCR products due to indels introduced by NHEJ. The PAM site and the sgRNA target site are indicated with the red and blue box, respectively.