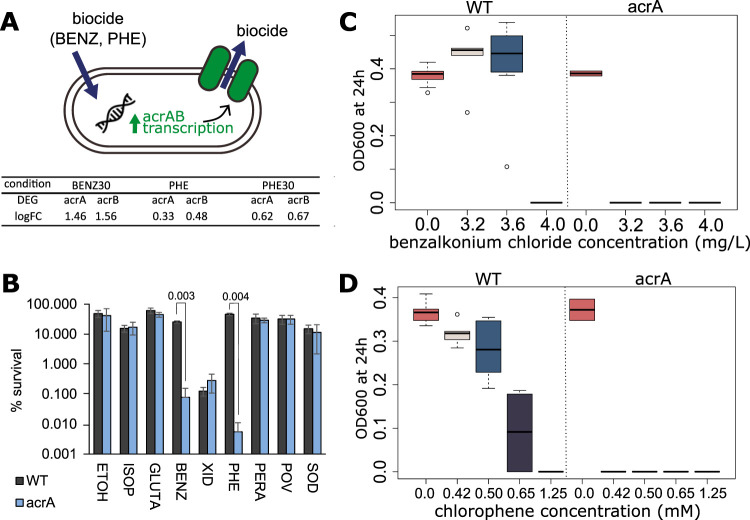
FIG 5.
Biocide susceptibility for the E. coli mutant with a knockout of the multidrug efflux protein gene acrA. (A) The genes for the multidrug efflux system AcrAB were upregulated after exposure to benzalkonium chloride and chlorophene. (B) Percent survival of the mutant acrA and parental strain (WT) exposed to the indicated biocides for 15 min. The concentrations were as follows: ETOH, 15% (vol/vol); ISOP, 11% (vol/vol); GLUTA, 125 μM; BENZ, 12.8 mg/liter; XID, 42 μM; PHE, 0.5 mM; PERA, 18 μM; POV, 33 μg/ml; SOD, 80 μM. Error bars represent the standard errors for biological duplicates, and the P values for significance are indicated at the top of the bars. (C and D) Growth at 24 h in the presence of the indicated concentration of the biocide in 96-well plates. (C) Benzalkonium chloride; (D) chlorophene. The definitions of the abbreviations are as follows: BENZ, benzalkonium chloride; XID, chlorhexidine gluconate; PHE, chlorophene; ETOH, ethanol; ISOP, isopropanol; GLUTA, glutaraldehyde; SOD, sodium hypochlorite; POV, povidone-iodine; SOD, sodium hypochlorite; WT, wild-type E. coli BW25113.